Transactions are the fundamental operations that allow the transfer of value between parties within a cryptocurrency network. The rise of cryptocurrencies has brought about a revolution in the way transactions are conducted and recorded. At the core of this revolution are two types of transactions: Onchain and Offchain. Understanding these concepts is essential for anyone interested in the cryptocurrency space, as they each offer distinct advantages and face unique challenges.
This guide aims to provide a clear and comprehensive introduction to on-chain and off-chain transactions, explaining how they work, their differences, and their respective roles in the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
Understanding Transactions
A transaction is an agreement between two parties to transfer a certain amount of cryptocurrency from one address to another. Transactions are verified through a process called validation, which ensures the integrity and authenticity of the transaction. Once validated, transactions are recorded in a public ledger, known as the blockchain.
How Transactions Work?
- Initiation: The sender creates a transaction request, specifying the recipient’s address and the amount to be transferred.
- Broadcast: The transaction request is broadcast to the cryptocurrency network.
- Validation: Network nodes validate the transaction using consensus mechanisms. These network nodes are incentivized via gas fees.
- Recording: Once validated, the transaction is recorded on the blockchain, making it a permanent part of the ledger.
What are Onchain Transactions?
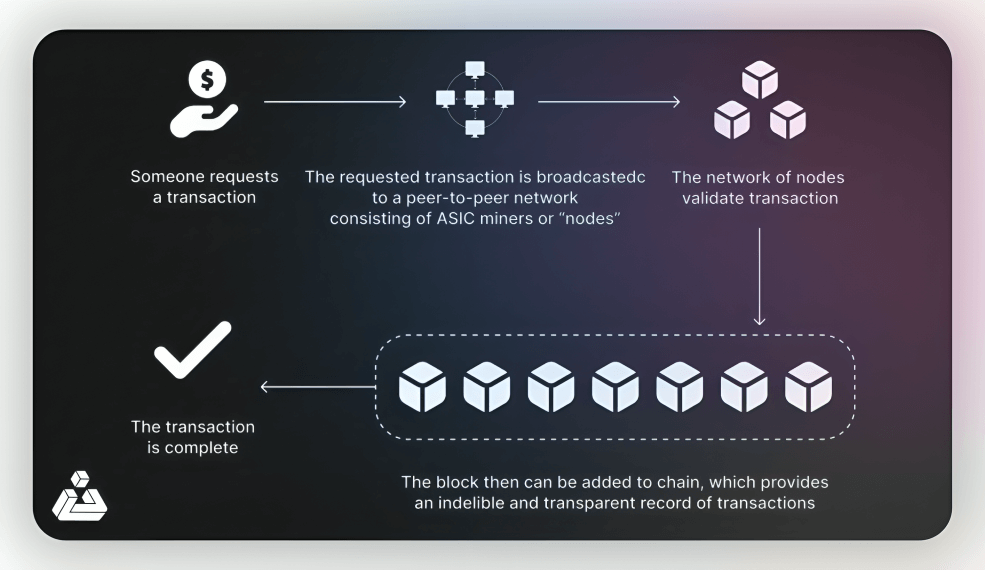
Onchain transactions occur directly on the blockchain. They are recorded and validated by the network’s nodes, ensuring a high level of security and transparency.
How Onchain Transactions Work?
- Broadcasting: When a user initiates an on-chain transaction, the details are broadcast to the network.
- Validation: The transaction undergoes a process of validation through consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS).
- Inclusion in Block: Once validated, the transaction is included in a block.
- Addition to Blockchain: The block is then added to the blockchain, providing immutability and transparency.
Advantages of Onchain Transactions
- Trustless Nature: Onchain transactions do not require intermediaries.
- Transparency: Every transaction is publicly visible and traceable.
- Security: High level of security due to the decentralized validation process.
Disadvantages of Onchain Transactions
- Speed: This can be slower due to the time required for validation.
- Cost: More costly because of transaction fees and resource-intensive validation.
- Scalability Issues: The growing size of the blockchain can lead to scalability challenges.
What are Off-chain Transactions?
Off-chain transactions occur outside the main blockchain network, facilitated by secondary layers or networks that operate independently of the main blockchain.
How Off-chain Transactions Work
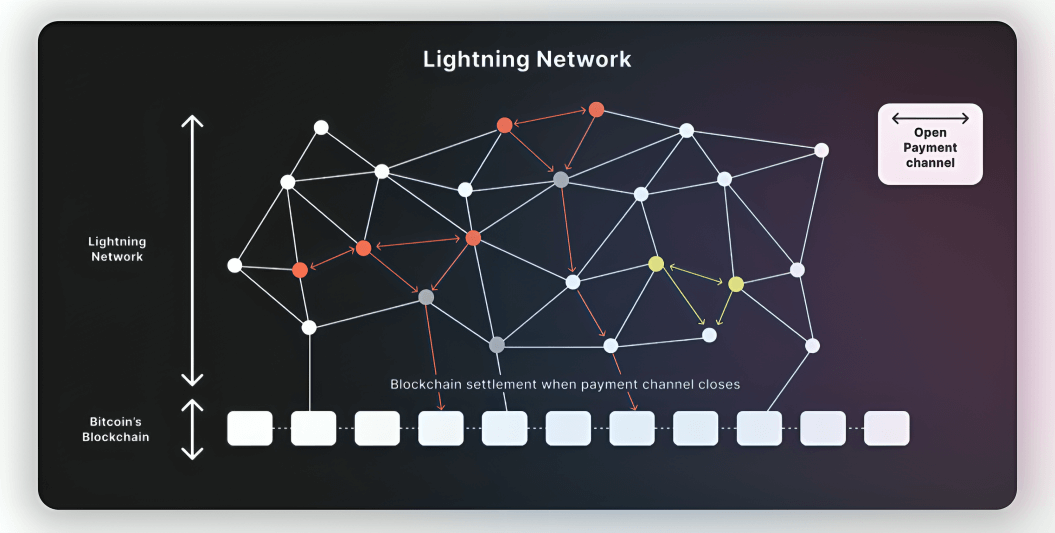
- Opening a Channel: Users open a payment channel by committing funds to a multi-signature wallet.
- Direct Transfers: Parties conduct multiple direct transactions within the payment channel.
- Settlement: After multiple transactions, the final state is broadcast to the blockchain for settlement.
To understand this better let’s consider Lightning Network, which enables users to open channels, allowing them to send multiple transactions to each other without waiting for the slower main net to confirm single exchanges.
Oracles play a crucial role in off-chain transactions by providing external data to trigger or validate transactions within these networks, ensuring they remain secure and reliable.
Advantages of Offchain Transactions
- Instant Execution: Transactions are executed instantly.
- Lower Fees: Reduced transaction fees compared to on-chain transactions.
- Increased Privacy: Transactions are not broadcast to the entire network.
Disadvantages of Offchain Transactions
- Complexity: This can introduce additional complexities.
- Security Vulnerabilities: Rely on the integrity of secondary layers or networks.
- Trust Dependencies: This may require trust in the off-chain network or intermediary.
Comparing Onchain and Offchain Transactions
While both on-chain and off-chain transactions serve the purpose of transferring value in the cryptocurrency ecosystem, they cater to different needs and use cases.
First, here are some key differences between on-chain and off-chain transactions:
| Key Differences | Onchain Transactions | Offchain Transactions |
| Visibility | Publicly visible on the blockchain | Not recorded on the blockchain; more private |
| Security | More secure due to the decentralized, transparent nature | More vulnerable to fraud and tampering |
| Scalability | Slower and more expensive, but more scalable over time | Faster and cheaper, but may lack long-term scalability |
| Reversibility | Irreversible | Can be reversed or canceled |
Use Cases Of Onchain Transactions
- High-value transfers where security and immutability are paramount.
- Smart contract interactions.
- Applications require a high level of trustlessness and transparency.
Use Cases Of Off-chain Transactions
- Microtransactions and frequent transactions where speed and cost-efficiency are more important.
- Instant payments in retail settings.
- Scenarios requiring high throughput and low fees, such as gaming applications.
Security Considerations
Security is a paramount concern in cryptocurrency transactions. on-chain transactions benefit from the inherent security features of the blockchain, including decentralization, cryptographic verification, and immutability. These attributes make on-chain transactions resistant to tampering and fraud, providing a high level of trust for users.
Off-chain transactions, however, must navigate the challenges of securing secondary layers or networks, which may introduce new attack vectors and trust dependencies. Ensuring the security of off-chain transactions often requires additional measures and vigilance.
Final Thoughts
The choice between on-chain and off-chain transactions depends on the specific requirements of the transaction. on-chain transactions offer unmatched security and trustlessness, making them ideal for high-value and critical transfers that demand transparency and immutability. off-chain transactions, on the other hand, provide scalability and efficiency advantages, catering to use cases that prioritize speed and cost-effectiveness.
For seamless integration of blockchain solutions into your business operations, explore Blockapex. We offer cutting-edge blockchain solutions tailored to enhance efficiency and security across various industries.
By understanding the differences, advantages, and considerations of on-chain and off-chain transactions, users can make informed decisions and choose the right transaction method for their cryptocurrency needs. As the cryptocurrency ecosystem continues to evolve, both on-chain and off-chain solutions will play crucial roles in addressing the diverse needs of users and enhancing the overall functionality and adoption of blockchain technology.
FAQs
- What are Onchain vs Offchain transactions?
Onchain transactions occur directly on the blockchain, where they are validated and recorded by network nodes, ensuring high security and transparency.
Off-chain transactions take place outside the main blockchain network, using secondary layers or networks to facilitate faster and cheaper transactions, which are later settled on the blockchain.
- What is an example of an off-chain transaction?
An example of an off-chain transaction is the use of the Lightning Network for Bitcoin. Users open payment channels and conduct multiple transactions off the main blockchain, and only the final state is recorded on the blockchain, enabling faster and lower-cost transactions.
- What is an on-chain transaction?
An on-chain transaction is a transfer of value that is recorded and validated directly on the blockchain. Once initiated, it is broadcast to the network, validated by nodes through consensus mechanisms, and permanently included in a block on the blockchain.
- What is Onchain vs Offchain governance?
Onchain governance involves decision-making processes and rules enforcement directly on the blockchain through smart contracts and voting mechanisms, ensuring transparency and immutability. Off-chain governance relies on external structures like forums, meetings, and off-chain agreements to make decisions, offering more flexibility but less transparency.
- Why are off-chain transactions cheaper?
Off-chain transactions are cheaper primarily because they do not require every transaction to be recorded and validated on the main blockchain. This reduces the computational and energy resources needed for each transaction, as well as the associated fees.