Some blockchain concepts might make you scratch your head unless you practically delve into them. Liquidity pools might sound confusing too, but they’re just a digital pot where you contribute your funds—like a collection of cryptocurrency or tokens locked in a smart contract, used to facilitate trading on decentralized exchanges.
In this blog, we have Max, a Web3 expert, and Anna, a curious beginner who is just trying to learn about liquidity pools like you. In this presentation, Max will cover what liquidity and liquidity pools are. Moreover, he will discuss how liquidity pools work, types of liquidity, and examples. Finally, Max will conclude with the pros and cons of liquidity pools.

What are Liquidity Pools?
Anna asks a critical question before Max begins to explain liquidity pools, “What is Liquidity?”
Max replies, “Liquidity refers to how easily an asset can be converted into cash without affecting its market price.”
Anna nods, “Can you give me an example?”
Max responds, “Sure, Imagine you are at a farmers’ market. The fruit stand sells apples, and there are many buyers and sellers. If you want to buy an apple, you can easily find someone to sell it to you, and if you want to sell your apple, there are many buyers ready to buy. This is a liquid market, where it’s easy to buy and sell because there’s a lot of activity.”
He further explains,”If a blockchain project has a lot of people trading its token, it’s considered liquid because it’s easy to buy and sell. If fewer people are trading it, the project might have low liquidity, making it harder to buy or sell without affecting the price.”
Anna now understands that liquidity is a fundamental part of crypto and financial markets. It is the way in which assets are converted to cash quickly and efficiently, avoiding drastic price swings. If an asset is illiquid, it takes a long time before it is converted to cash.
Max now proceeds to give a presentation on Liquidity pools. Come let’s watch it with Anna. 
A liquidity pool is a collection of cryptocurrencies or digital assets that facilitate financial transactions like swapping, lending, and earning yield. Users who contribute assets to liquidity pools earn rewards, driving liquidity to decentralized applications (DApps) and enabling them to compete with centralized services. As decentralized finance (DeFi) grows, it has the potential to outpace traditional financial systems.
Think of a community pot where everyone contributes apples (Token A) and oranges (Token B). Anyone can come to the pot to trade apples for oranges or vice versa. The more apples and oranges in the pot, the easier it is for people to trade without running out.
Similarly, in a liquidity pool, users deposit cryptocurrencies (like ETH and USDT), allowing others to swap between them easily. Those who contribute to the pool earn rewards, like a share of the trading fees, as an incentive for providing liquidity.
Liquidity Pools: Importance and Use Cases

Liquidity pools are essential for powering decentralized finance (DeFi), enabling seamless token swaps, and providing constant liquidity for various financial activities. They also reward users for contributing to market efficiency and accessibility.
Key Use Cases of Liquidity Pools
Token Swaps:
Facilitate instant cryptocurrency exchanges on decentralized exchanges (DEXs) like Uniswap and PancakeSwap.
Yield Farming:
Liquidity providers can stake their pool tokens to earn additional rewards, maximizing returns.
Lending and Borrowing:
Platforms like Aave use liquidity pools to match borrowers and lenders seamlessly.
Stablecoin Transactions:
Enable efficient transfers and conversions between stablecoins like USDT and DAI.
Synthetic Assets:
Support the creation of tokenized assets that mimic the value of real-world commodities or stocks.
Cross-Chain Interoperability:
Provide liquidity for bridging assets across different blockchains, enhancing connectivity in the crypto ecosystem.
Insurance:
Power decentralized insurance platforms by pooling funds to cover claims in case of predefined risks.
Efficient Governance:
Token holders in liquidity pools often gain voting power in DeFi protocols, enabling decentralized decision-making.
Tranching:
Facilitate risk segmentation by allowing users to invest in different tranches with varying levels of risk and reward, catering to diverse financial strategies.
How do Liquidity Pools work?
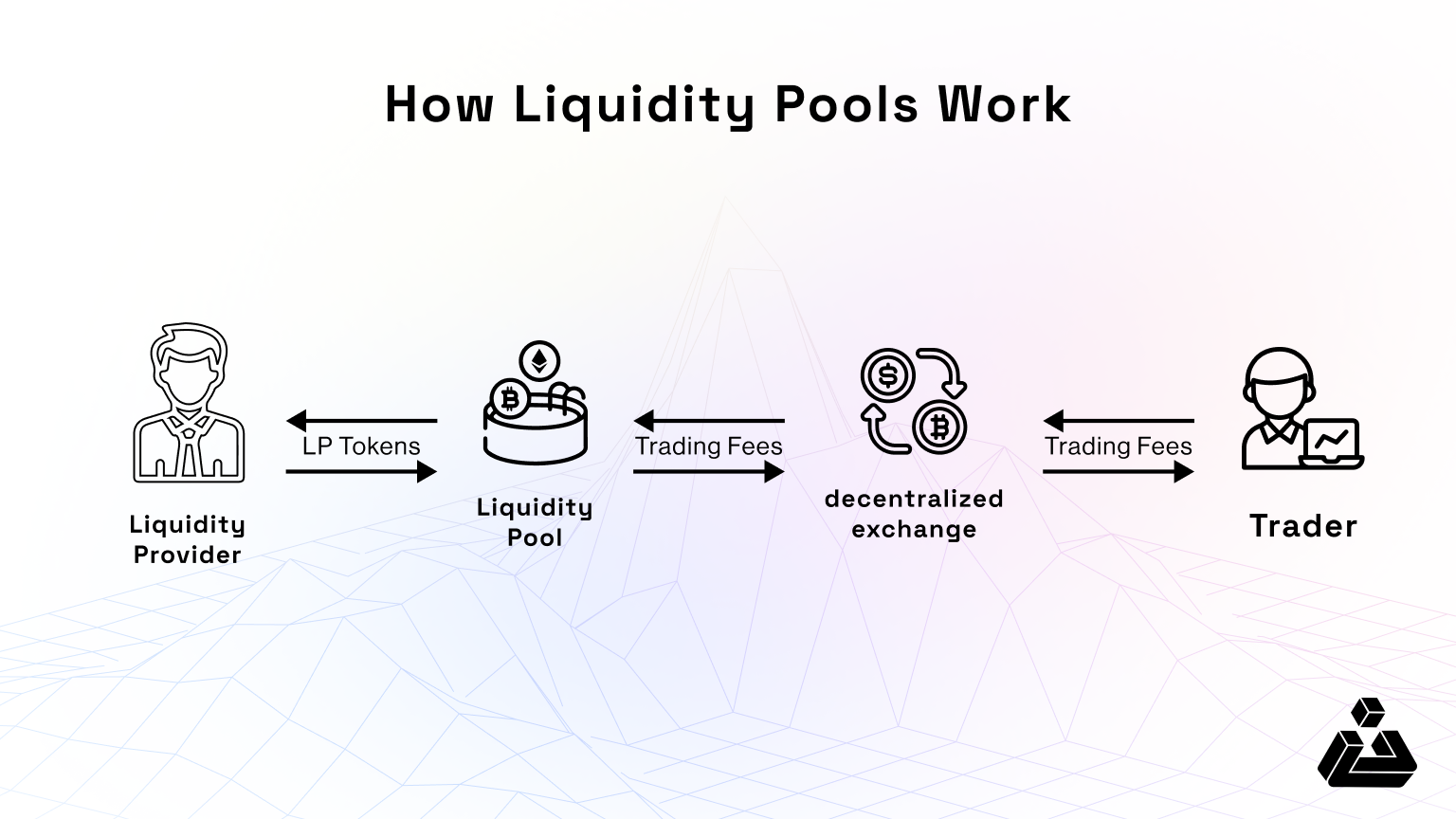
As mentioned earlier, a liquidity pool incentivizes users to stake their digital assets by offering rewards. These rewards can include crypto tokens, a share of trading fees, or governance rights.
Here’s a step-by-step example of how it works, using an ETH-DAI liquidity pool on Uniswap:
- Visit Uniswap:
Go to the Uniswap platform. - Locate the ETH-DAI Liquidity Pool:
Search for the ETH-DAI pool in the liquidity section. - Deposit Assets in a 50/50 Ratio:
Contribute an equal value of ETH and DAI to the pool. For example, if you want to invest $10,000, deposit $5,000 worth of ETH and $5,000 worth of DAI. - Receive Liquidity Provider Tokens (LPTs):
After depositing, you’ll receive ETH-DAI LPTs, which represent your share in the liquidity pool. - Stake LPTs for Additional Rewards:
Stake your LPTs in a staking pool to earn additional rewards. Many platforms offer native tokens like UNI as an incentive. - Earn Fees and Staking Rewards:
- Earn a portion of the transaction fees collected from traders using the ETH-DAI liquidity pool.
- Receive UNI tokens as rewards for staking your LPTs, depending on the lock-up duration you agreed to (e.g., one week or three months).
By participating in the ETH-DAI liquidity pool, you benefit from trading fees while simultaneously earning platform-specific incentives like UNI tokens.
Anna, enjoying the presentation, asks, “What determines the rewards or fees I earn as a liquidity provider in a pool like ETH-DAI on Uniswap?”
Max replies, “As a liquidity provider in a pool like ETH-DAI on Uniswap, you earn rewards from two main sources: trading fees and staking rewards. Trading fees are a percentage of each transaction, distributed based on your share in the pool. Staking your liquidity provider tokens (LPTs) in a staking pool earns you extra rewards, often in platform tokens like UNI, for securing the pool and incentivizing long-term participation.”
Types of Liquidity Pools

Max continues to explain different type of liquidity pools:
Single-Asset Liquidity Pools:
Users deposit a single type of asset, like ETH or USDT, and earn rewards based on its use in the pool.
Example: Yearn.finance (provides yield farming pools for various assets).
Dual-Asset Liquidity Pools (or Token Pairs):
Users deposit two different assets, like ETH and USDT, in equal value to provide liquidity.
Example: Uniswap, SushiSwap, PancakeSwap (ETH-USDT, BTC-USDT pairs).
Stablecoin Liquidity Pools:
These pools involve stablecoins (e.g., USDC, DAI) and are designed to minimize volatility.
Example: Curve Finance (focuses on stablecoin swaps like DAI-USDC).
Multi-Asset Liquidity Pools:
Pools that support more than two assets, allowing users to provide liquidity to a more diversified set of assets.
Example: Balancer (supports pools with multiple tokens).
Synthetic Asset Pools:
Pools are designed to support synthetic assets, which mimic real-world assets like stocks or commodities.
Example: Synthetix (provides liquidity for synthetic assets such as sUSD, sBTC).
Popular Liquidity Pool Providers
Decentralized platforms use automated market makers (AMMs) to facilitate seamless and permissionless trading through liquidity pools. Some of the most prominent platforms built around liquidity pools include:
- Uniswap: An open-source exchange enabling users to trade ETH for any ERC-20 token without a centralized intermediary. It allows anyone to create an exchange pair on the network free of cost.
- Curve: A decentralized liquidity pool platform optimized for stablecoin trading on Ethereum, offering reduced slippage due to stablecoins’ low volatility.
- Balancer: A decentralized platform offering various pooling options, including private and shared liquidity pools, with tailored benefits for liquidity providers.
Pros and Cons of Liquidity Pools
Pros:
- Enables real-time trading at market prices on decentralized exchanges (DEXs).
- Rewards liquidity providers with interest, rewards, or annual percentage yield (APY) on their assets.
- Uses transparent, publicly verifiable smart contracts for security audits.
Cons:
- Pools are often managed by a small group, which conflicts with decentralization principles.
- Susceptible to hacking due to weak security measures, risking losses for liquidity providers.
- Vulnerable to fraud, including rug pulls and exit scams.
- Exposes liquidity providers to impermanent loss, where price fluctuations of pooled assets cause unrealized losses compared to holding them directly.
Max concludes the presentation by adding in final words, “By 2025, DEXs are expected to offer deeper liquidity through improved Automated Market Makers (AMMs), liquidity pools, and cross-chain trading capabilities. Enhanced user interfaces and better integration with traditional financial systems will make DEXs more accessible to a broader audience.”
Max: “Liquidity pools power DeFi, enabling efficient swaps and rewarding contributors. Hands-on participation not only deepens understanding but also helps build a stronger ecosystem!”
Anna eagerly interjects, “So, a workshop next time maybe?”
Max laughs, “Sure, why not. Please ask any questions related to liquidity pools”
FAQs
- Anna: What happens if the value of my tokens changes while they’re in the pool?
Max: That’s called impermanent loss, Anna. If token prices fluctuate significantly compared to when you deposited them, you might earn less than if you had just held the tokens.
- Anna: Can liquidity pools be risky?
Max: Yes, there are risks like: - Impermanent loss
- Smart contract vulnerabilities
- Rug pulls if the pool is run by bad actors.
However, researching reliable platforms can help reduce these risks.
- Anna: Where should I start if I want to contribute to a liquidity pool?
Max: Begin with smaller, stablecoin pools on well-known platforms like Uniswap. They’re beginner-friendly and come with lower risks.
Conclusion
BlockApex is at the forefront of leading innovation, publishing insightful blogs, and providing the best blockchain solutions. React to us today!