Imagine putting your money into a savings account in a traditional bank and earning interest from it. Just as you deposit money into a bank account and earn interest over time, in staking, you lock up digital assets to support blockchain network operation and in return earn rewards, akin to interest payments.
Similar to a community potluck, where everyone brings a dish to share and maintain the event together. Instead of trusting a single party, the event is managed by everyone who attends. Participants receive rewards based on their contribution to the event’s success but there is no central authority to fix things if something goes wrong.
In this article, we’ll overview DeFi, unlock the core concept of DeFi staking, and learn the types of staking in DeFi. Moreover, we’ll cover benefits and risks of DeFi staking. Lastly, we’ll see the steps to participate in DeFi staking.
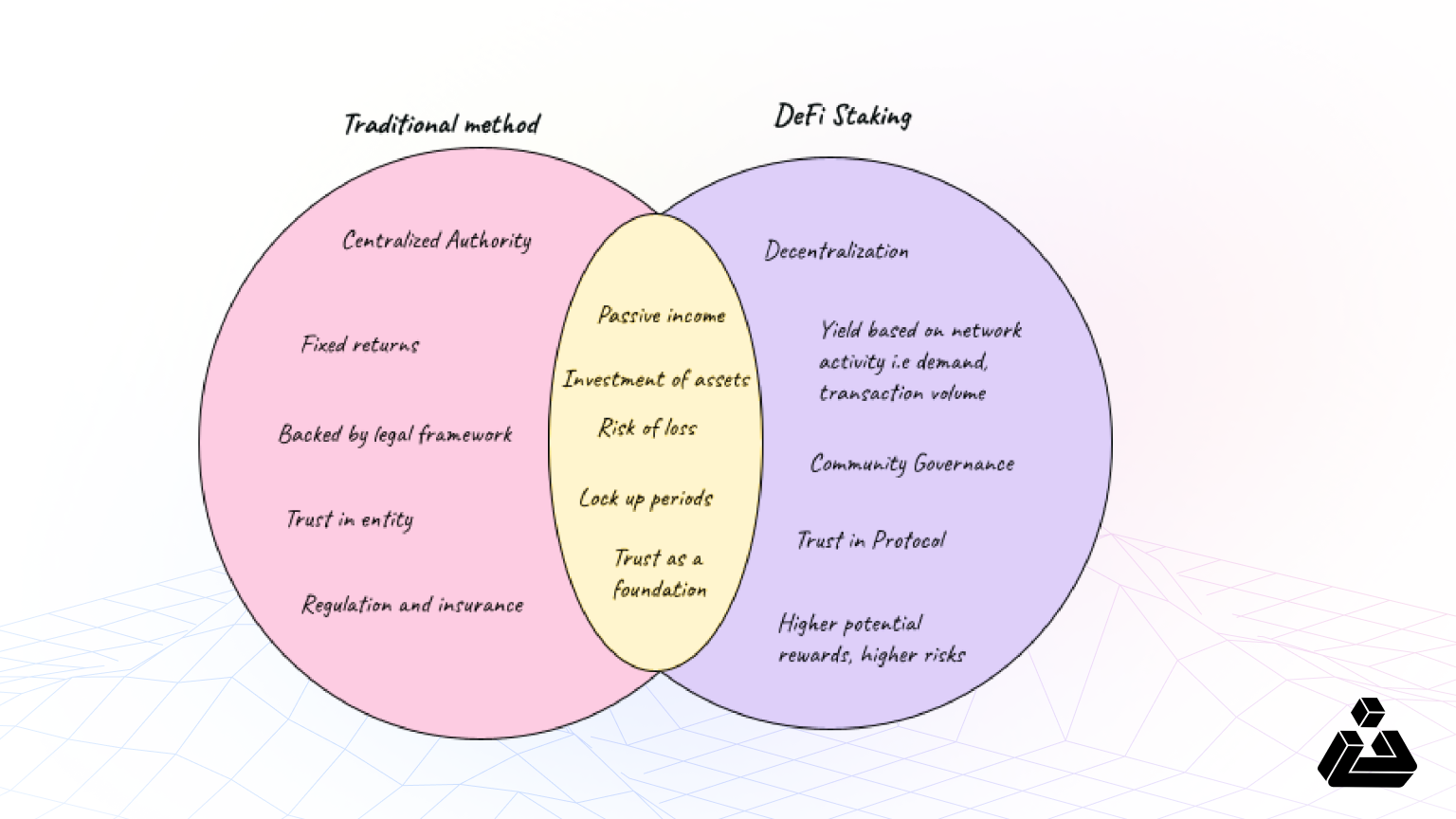
What is DeFi Staking?
Decentralized Finance, known more commonly as DeFi, is an emerging model for organizing and enabling cryptocurrency-based transactions, exchanges and financial services. It eliminates the idea of middleman entirely and operates under the idea of open, direct finance.
Financial transactions or agreements are bound by smart contracts, self-executing pieces of code, automating and enforcing rules when certain conditions are met rather than being dictated or governed by a central authority. The transactions cannot be reversed as they are by nature immutable on blockchain.
Market Size of DeFi
DeFi provides a wide range of services such as yield farming, insurance, staking, decentralized exchanges (DEX), borrowing and lending. This wide range of services is also expected to grow demand for DeFi technology in the forecast period.
Decentralized finance market size was valued at USD 19.67 billion in 2024 and is likely to cross USD 2.55 trillion by 2037, registering more than 45.4% annual growth rate (CAGR) during the forecast period i.e., between 2025-2037.
Understanding DeFi Staking
Technically speaking, DeFi staking involves locking cryptocurrency assets into smart contracts to earn rewards and generate passive income. These assets can be both fungible or non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and the rewards usually correspond to earning more of the same.
It’s a great way to incentivize cryptocurrency investors to hold on to their assets while earning high interests. DeFi staking appeals to those seeking substantial gains, though it comes with higher risks due to market volatility and security concerns.
No advanced trading skills are required, however choosing a secure platform is key. Unlike Proof of Work (PoW) systems that require heavy computing power, DeFi staking relies on Proof of Stake (PoS) networks, where validators who stake their assets confirm transactions.
Different types of DeFi Staking
Now that we have understood the core concepts about DeFi staking, it is time to take a closer look at the types of DeFi staking available for users.
Yield Farming
With the rise of yield farming, the true power of DeFi became evident. The term yield farming is referred to the practice of moving multiple crypto assets over DeFi staking platforms in order to churn out the maximum profit by the user. In order to achieve this, users make their assets available on a lending platform or a liquidity pool. Interest is the form in which they earn their passive income and sometimes it is also earned via a portion of the revenue generated by their DeFi staking platform of choice.
Liquidity Staking
Users provide equal amounts of two cryptocurrencies to a liquidity pool on a decentralized exchange (DEX) or automated market maker (AMM). In return, they earn a share of transaction fees proportional to their contribution. This approach supports market liquidity while generating passive income.
Governance Staking
Users lock cryptocurrencies to earn governance tokens, granting them voting rights on platform proposals. Voting power depends on the number of tokens staked, allowing users to influence the platform’s future direction.
Validator Staking
Users stake cryptocurrencies to run validator nodes that verify transactions and secure the network. Validators are rewarded with crypto for adding blocks to the blockchain, ensuring network integrity.
NFT Staking
Users stake their Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) on decentralized platforms to earn rewards while retaining ownership of the NFTs. This method turns digital collectibles into passive income opportunities.
Steps to participate in DeFi Staking
Before staking crypto, it is a good idea to check mark a few factors which might influence your decision, including:
Minimum staking amount:
You may be required to stake a minimum amount which might be significant. Not every network requires this, but one way of getting around it is pool staking, which means you pool your assets with others in order to get past the minimum staking amount. However not every platform allows pool staking.
Locked tokens:
Since your assets are locked for a period of time, which prevents you from selling or using them, you need to make sure that lock up period aligns with your needs. Otherwise, you may want to consider liquid staking, which provides you representative tokens that you can sell or use.
Crypto rewards:
When staking crypto, prior research is required to understand a few parameters like annual percentage yield, which can fluctuate based on a number of metrics, including the number of assets you have staked. Moreover, looking into frequency of staking reward distributions and general crypto knowledge will be required.
Technical requirements and skills for staking crypto:
Running a validator node often requires specific skills, reliable hardware, a stable internet connection, and consistent online availability. If these requirements are challenging to meet, delegated staking may be a more suitable option.
Regulatory and tax concerns:
Depending on your location, staking may be subject to strict regulations, including taxes on staking rewards. Additionally, the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has expressed concerns about crypto staking, especially regarding cryptocurrency exchanges not fully disclosing potential risks to users.
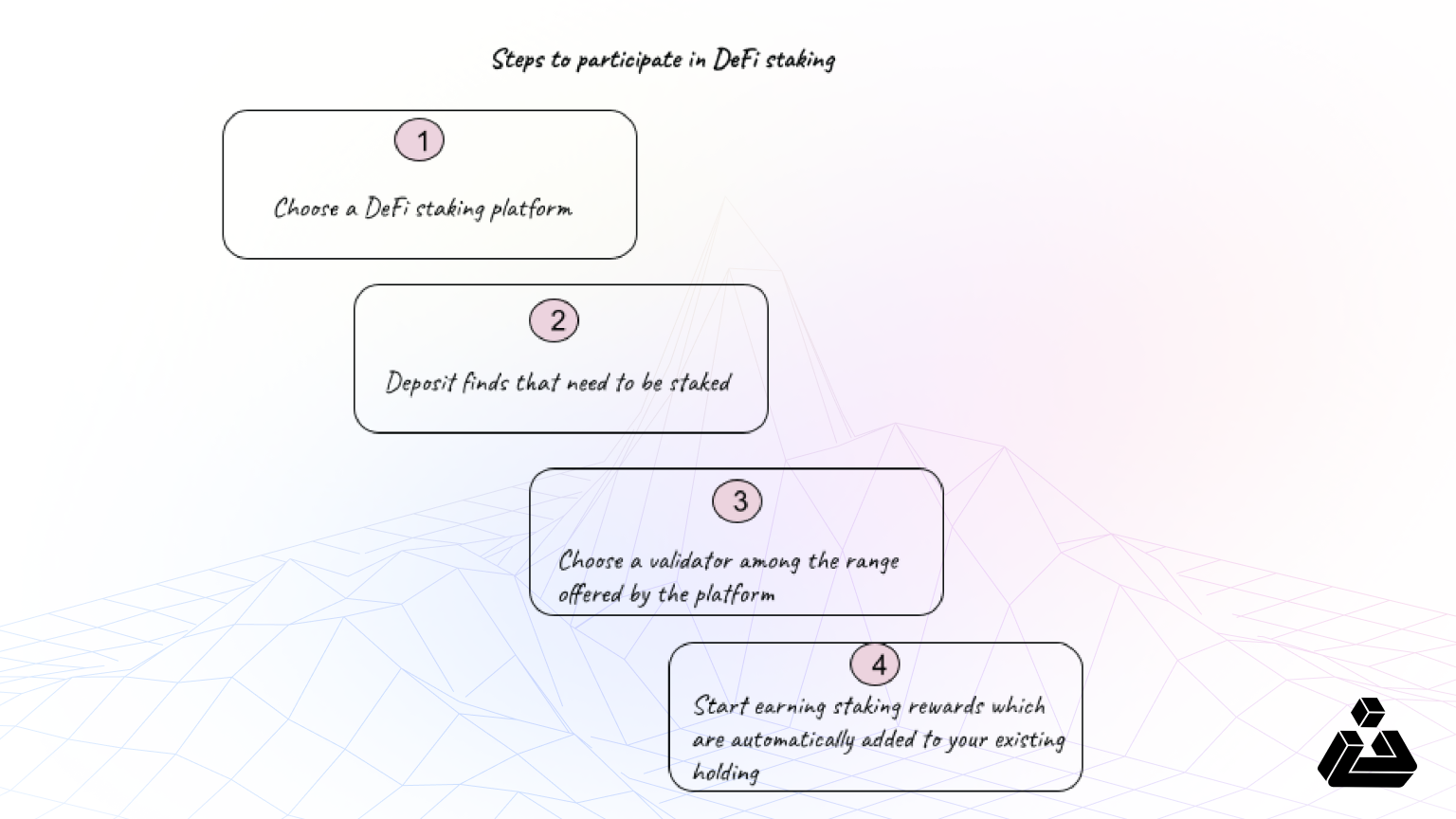
While the steps above might be clear enough, a 5th step of unstaking is always available for users to withdraw their deposited funds.
Unstaking refers to the process of withdrawing your staked cryptocurrency from a DeFi staking platform. When users stake tokens, their assets are locked into the protocol to support network operations or liquidity, and unstaking involves reversing this process.
Each platform has unique policies around unstaking, which can include lock-up periods, fees, or instant withdrawal options. Let’s understand this with an example of staking and unstaking funds via Lido Finance, A liquid staking platform.
Step 1: Choose a Platform
Alice decides to stake her Ethereum and selects Lido Finance, a platform known for offering flexible staking without lock-up periods.
Step 2: Deposit Funds
She connects her crypto wallet i.e Metamask and deposits 1 ETH into the Lido staking pool.
Step 3: Receive stETH
In return for staking her ETH, Alice receives stETH tokens, which represent her staked ETH and automatically grow in value as staking rewards accumulate.
Please note that all platforms don’t issue derivative tokens like stTokens. When staking AAVE tokens, users don’t receive a separate stToken rather their balance is being updated to reflect the rewards they have earned. The latter is an easier option for beginners as it saves them from the hassle of managing different parts.
Step 4: Earn Rewards
While her ETH is staked, Alice enjoys staking rewards that are reflected in the increasing balance or value of her stETH tokens. These rewards are added without her needing to take any extra steps.
Step 5: Withdraw Anytime
If Alice decides to unstake, she can:
- Trade stETH for ETH on decentralized exchanges like Uniswap instantly, ensuring liquidity.
- Alternatively, Lido supports direct withdrawal, she can withdraw her ETH directly without any lock-up period.
Frequently Asked Questions
In this section, you will find answers to the most common questions about staking crypto.
- What are the benefits of staking crypto?
Staking crypto provides a variety of benefits:
- Generating passive income in case you decide to stake your token long-term
- Enhanced network security
- Potential application of rewards
- Better energy efficiency when compared to mining
- What are the risks of staking crypto?
Some of the risks associated with staking your assets include:
- Limited or no liquidity during the lockup period, which restricts access to your funds
- Staking rewards can fluctuate due to price changes or validator performance
- Assets may be confiscated if there’s a protocol violation
- Potential future regulations may impact staking rewards, add new taxes, or even affect legality
- Advanced technical knowledge may be required for certain types of staking
- Is Staking Crypto Safe?
Staking is generally safe, especially compared to other crypto activities, but it does come with important considerations. To enhance safety, keep these tips in mind:
- Stake only on reputable, secure blockchain networks
- When staking through validators, choose ones with a reliable track record
- Use platforms and wallets that offer strong security features and encryption
- Be prepared for cryptocurrency market volatility, as returns are not guaranteed
The Bottom Line
DeFi staking is an investment to be done carefully, but it promises huge returns in the longer-run. Market volatility, liquidity constraints, regulatory changes and protocol risks may pose some risks and that is why a thorough assessment should be conducted prior to investing.