Upon hearing these two words; Blockchain and Telecom, one may struggle to find any connection between them, assuming they belong to entirely different realms, like two galaxies in different universes. However, the reality is far more intertwined, Blockchain in Telecom is not coexisting but is unlocking mind-blowing possibilities.
Telecommunications, the exchange of information over distances, encompasses technologies such as radio, telephone, television, satellite, microwave, data communication, and networking. Simply put, it includes all technologies stemming from telecom advancements like satellite internet coverage, 5G, and upcoming 6G. Blockchain, a decentralized digital ledger, is now making significant inroads into this field.
In this article, we will probe into the key characteristics of blockchain technology, the benefits of blockchain in telecom, blockchain use cases for telecom, and real-world projects that are truly astonishing. Trust me, you don’t want to miss out on the real scoop. We will also explore the challenges and future possibilities, such as the role of blockchain in 6G and mega projects like Starlink by SpaceX.
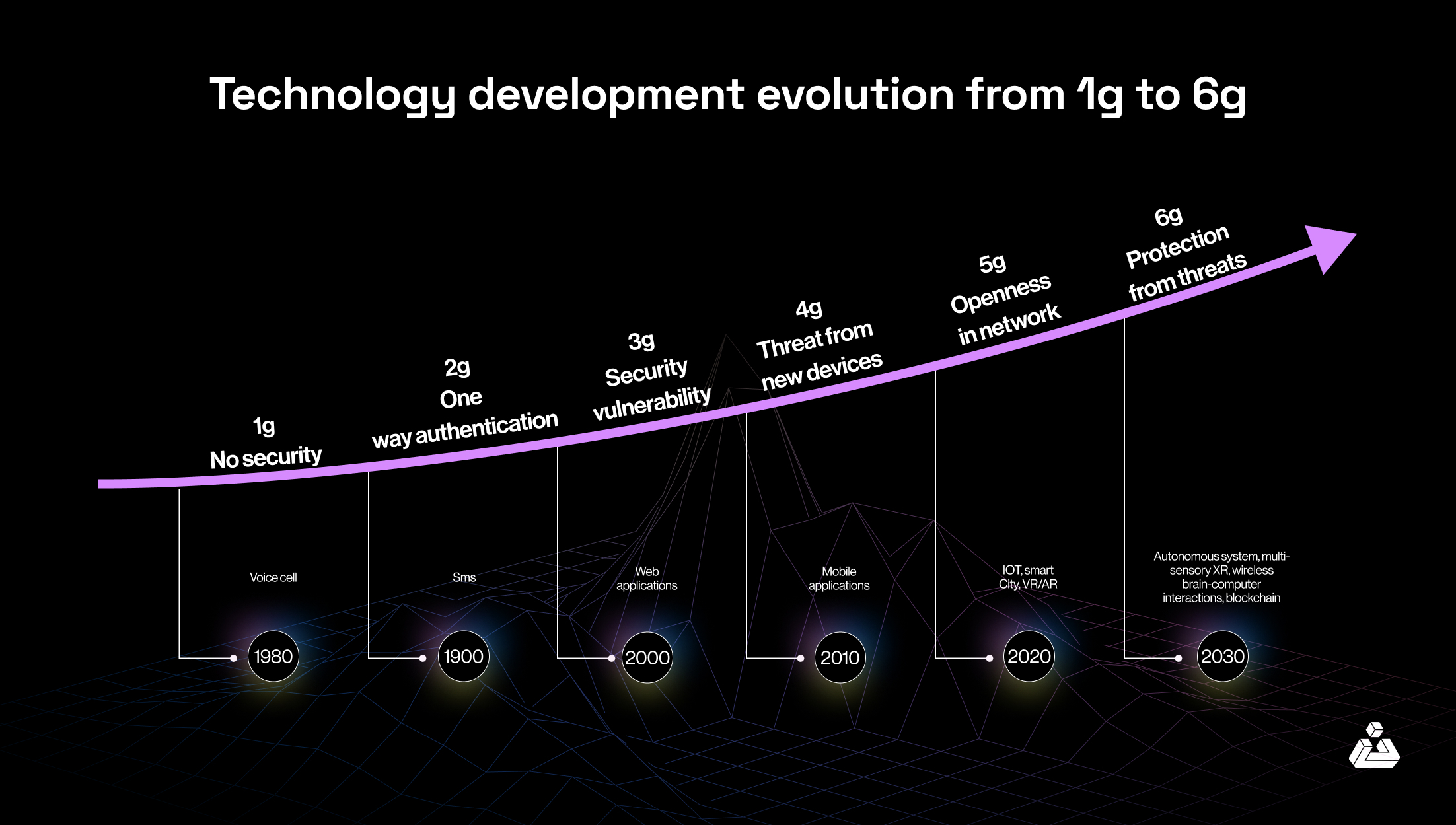
Evolution from 1G to 6G
Introduction to Blockchain in Telecommunications
Blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger technology that optimizes processes, transactions, and security measures. In telecommunications, it introduces a transparent, tamper-proof way of recording and managing data and transactions across IP networks, enabling fast upload, download speeds, and all forms of communication (voice, text, video, email) through smartphone apps.
Key characteristics of Blockchain
It is essential to build an understanding of the distinct features of blockchain to see how they will benefit the telecom sector as we delve deeper into the discussion later in the article. Let’s explore the key characteristics of blockchain.
- Distributed Ledger: All participants have access to the entire ledger, not just parts related to their transactions.
- Digital Nature: Blockchains are digital, unlinked to physical assets, enabling their use in digital currencies like Bitcoin.
- Near Real-Time Updates: Digital transactions and ledger updates can occur almost in real time.
- Chronological and Timestamped: Transactions are recorded chronologically with exact timestamps.
- Cryptographically Sealed: Each block is linked to the previous block with cryptographic headers, making data tamper-proof.
- Irreversible and Auditable: Once finalized, blocks cannot be altered, simplifying auditing.
- Trustless Operation: No central authority is needed; transactions are authenticated through methods like proof of work or proof of stake.
- Fewer Third Parties: Blockchain’s distributed ledger reduces the need for third-party mediators, lowering costs and complexity.
Also Read: Advanced Cryptographic Techniques in Blockchain
Benefits of Blockchain in Telecom
Blockchain is positioned as a disruptive technology that could revolutionize system interactions, making transactions cheaper, more transparent, and more efficient. Let’s have a look at the benefits that blockchain can provide to telecom and how its key characteristics aid in addressing many fundamental problems in the telecom sector.
Improved connectivity:
Blockchain enhances connectivity by decentralizing the network, which streamlines communication. By leveraging distributed ledger technology, telecom networks can reduce latency and improve the efficiency of data transmission across different nodes.
Increased transparency:
Blockchain provides a clear, immutable record of transactions, making operations more transparent. Telecom operators can use blockchain to track and verify inter-network billing transactions, ensuring accuracy and reducing billing conflicts.
Greater security:
In 5G networks, blockchain secures data exchanges and prevents unauthorized access, mitigating risks of centralized attack points. Therefore, it enhances security through cryptographic techniques and decentralization.
Enhanced customer experience:
Blockchain enables telecom providers to offer personalized services and streamlined customer support through smart contracts and efficient data management. It optimizes service delivery, adding to overall customer satisfaction.
Cost savings:
Automating processes and eliminating intermediaries yield in reducing operational costs. As blockchain reduces clearing house fees, and administrative costs in inter-network billing through smart contracts, which verify and automate transactions without manual intervention.
Improved Interoperability:
Blockchain enables seamless interaction between various networks and platforms, facilitating better data exchange and cooperation among telecom operators.
After viewing the complete picture of combined blockchain characteristics and benefits, we can further discuss the potential use cases.
Use cases of Blockchain in Telecom
As the telecom industry ushers in the 5G era, blockchain technology emerges as a pivotal enabler, promising to transform various facets of the sector. Here are some innovative blockchain use cases that illustrate how this technology can enhance efficiency, security, and customer experience in telecom.
Identity Management
The traditional KYC (Know Your Customer) process is cumbersome and involves sensitive information stored with third parties, making it vulnerable to breaches and fraud.
Blockchain can store customer identities in a decentralized, immutable ledger. This approach enhances security by eliminating the central point of failure and provides customers with a portable, tamper-proof digital identity.
Imagine a customer setting up a new account with a telecom provider. Since their identity details are securely stored on a blockchain, they will be able to authenticate themselves quickly and safely with other service providers without repetitive or manual paperwork or KYC processes.
5G Enablement
The proliferation of IoT devices with 5G introduces challenges related to secure, real-time data transmission and device management.
Blockchain can act as a secure data backbone for 5G networks, ensuring data integrity and automating real-time information exchange among interconnected devices.
In a smart city, blockchain technology can secure data from self-driving vehicles, ensuring that information about their movements and sensor data remains accurate and tamper-proof, which is critical for safety and operational efficiency.
Interconnect Billing
The current interconnect billing process encounters significant challenges: clearing houses add complexity and high costs to billing, creating delays and administrative burdens. They also obscure visibility, leading to potential disputes between home and roaming network operators. Furthermore, operators incur significant fees for clearinghouse services, and transitioning to a blockchain system necessitates developing new standards and strategies for effective implementation.
To address these challenges, a private blockchain network can be implemented where roaming and home network operators share CDRs directly, removing the need for a clearing house and reducing associated costs. Blockchain enables real-time sharing of CDRs, which accelerates billing and settlement processes while enhancing transparency and reducing disputes.
Smart contracts on the blockchain automate settlement processes, further streamlining operations. Developing standards for blockchain interoperability and applying cryptographic techniques ensure secure management and privacy of CDR data.
Challenges in Blockchain Integration with Telecom
Blockchain for telecommunications faces multiple challenges that need to be dealt with with careful consideration and strategic planning. Overcoming integration hurdles, ensuring scalability, complying with regulations, fortifying security, and managing costs are pivotal for successful implementation. Thus, addressing these challenges will pave the way for blockchain’s transformative potential in revolutionizing the telecom industry.
Integration:
Integrating blockchain and telecom poses issues due to its complex nature. Expertise and resources are required for seamless integration as well as to ensure compatibility, there is demand for careful planning and execution.
Scalability:
Blockchain itself encounters scalability issues as it is not able to handle the increased volume of transactions at once. Concepts like Layer 2 solutions, sharding, and advanced infrastructure including the Blockchain Operating system may be required to handle scalability issues.
Regulatory Compliance:
Adhering to evolving legal frameworks while maintaining blockchain’s decentralized nature can be intricate. Going through complex compliance standards across different regions is a must, to ensure data privacy and security measures align with regulatory mandates.
Security:
While blockchain is known for its strong security, challenges remain in the telecom sector. Protecting against advanced cyber threats requires ongoing vigilance, robust encryption methods, and effective consensus mechanisms to secure sensitive data.
Cost:
Integrating blockchain into telecommunications can be costly. It involves significant investments in technology, expertise, and infrastructure, alongside expenses for upgrading systems and training personnel.
Future Insights: Blockchain’s Role in Telecom Projects
This section delves into pioneering real-world projects that exemplify how blockchain is being applied to address challenges and create opportunities within the telecom sector. Stay here a little more because I promise it gets even more fascinating by the time you reach the end of this section. Let’s see how these real-world projects share an interesting synergy between blockchain and telecom.
-
Starlink by SpaceX

Cryptosat’s Crypto1, the first crypto satellite, has already been launched aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket as part of the Transporter 5 mission. This compact satellite aims to provide a tamper-proof platform for securing and launching blockchains and Web3 platforms from space. Cryptosat co-founder Yonatan Winetraub noted that their satellite will offer cryptographic services without interfering with other satellites. Yan Michalevsky, another co-founder, emphasized that Crypto1 will serve as an off-world ‘root-of-trust,’ enabling secure cryptographic functions such as zero-knowledge proofs and potentially hosting an entire blockchain in space.
Starlink is a satellite internet constellation developed by SpaceX, aiming to provide high-speed, low-latency internet globally, especially to underserved areas. Owned by SpaceX, and founded by Elon Musk, it uses low Earth orbit satellites for faster and more reliable connectivity, with a scalable network that leverages SpaceX’s reusable rocket technology for cost-effective deployment.
Given that, Blockchain technology is being explored to enhance the management and logistics of satellite internet projects such as SpaceX. For example, IBM’s collaboration with Cloud Constellation and LeoStella utilizes a consortium-based blockchain network where participants—satellite service providers, manufacturers, suppliers, launch service providers, mission control centers, and satellite operations centers—share an immutable ledger of transactions.
Applying blockchain technology to these use cases involves:
- Networks: Consortium of participants in a peer-to-peer network
- Participants: Satellite service provider, satellite manufacturer, suppliers, launch service provider, mission control center, and satellite operations center
- Channels: Access control mechanisms that isolate transactions between participants
- Assets: Data structures like satellite parts and documents
- Smart Contracts: Algorithms and business logic governing transactions
- Transactions: Invocations of algorithms for various processes
This blockchain approach streamlines complex processes, builds trust, accelerates operations, reduces costs, and enhances safety, paving the way for more reliable and scalable satellite internet coverage.
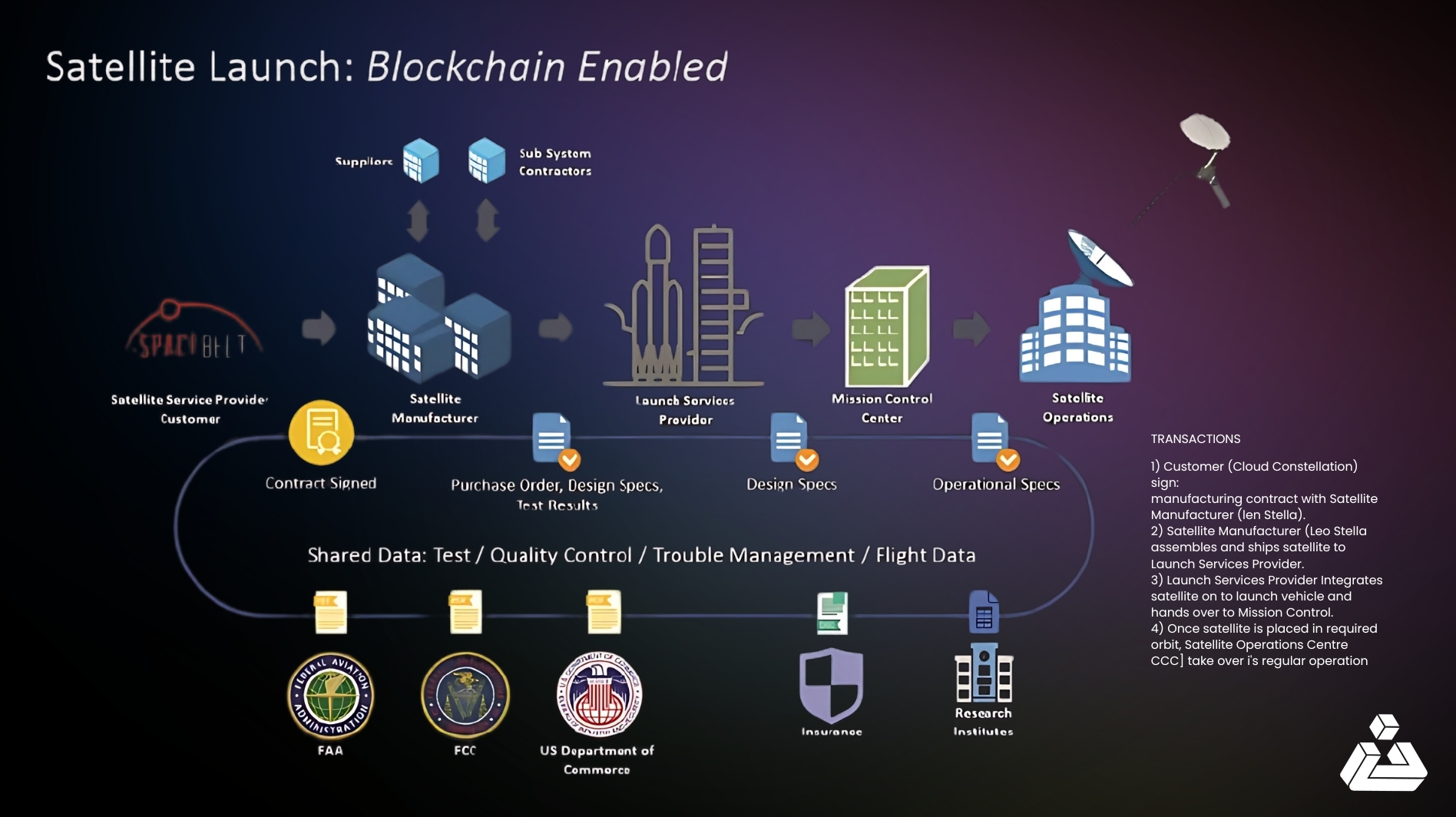
-
5G Development
The time is not too far when Blockchain will be completely implemented in 5G technology as researchers have found that blockchain technology can significantly enhance 5G’s transformative capabilities, which offer speeds up to 20x faster than 4G. Here’s how blockchain integrates with and amplifies 5G:
- Enhanced Security: Blockchain’s decentralized and cryptographic features provide robust protection against unauthorized access and data breaches in the highly connected 5G network.
- Trusted Connectivity: 5G’s high-speed, reliable connectivity supports blockchain’s secure device communication, enabling verified, peer-to-peer transactions and smooth IoT integrations.
- Scalability Boost: 5G’s high bandwidth and low latency address blockchain’s scalability issues, facilitating faster transactions and overall improved performance.
Use Cases and Developments:
- Supply Chain Management: Combining blockchain’s transparency with 5G’s real-time tracking streamlines supply chains, enhancing efficiency and authenticity.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Blockchain and 5G together unlock advanced IoT applications, leading to smarter cities and better asset management.
- Telecommunications and Identity Management: Blockchain improves identity management and privacy in telecoms, while 5G ensures fast, secure communication.
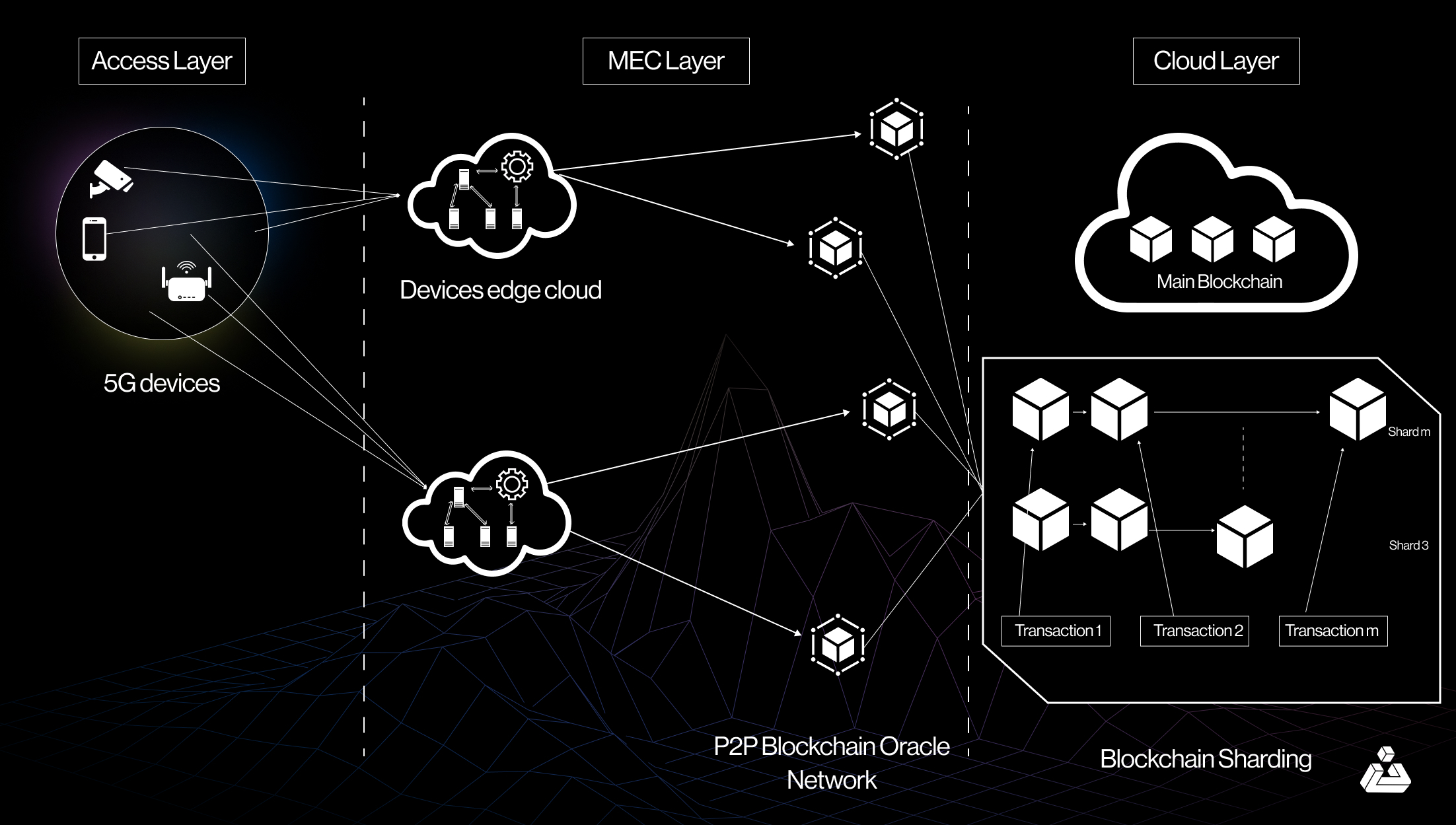
Overview of Blockchain and 5G system
-
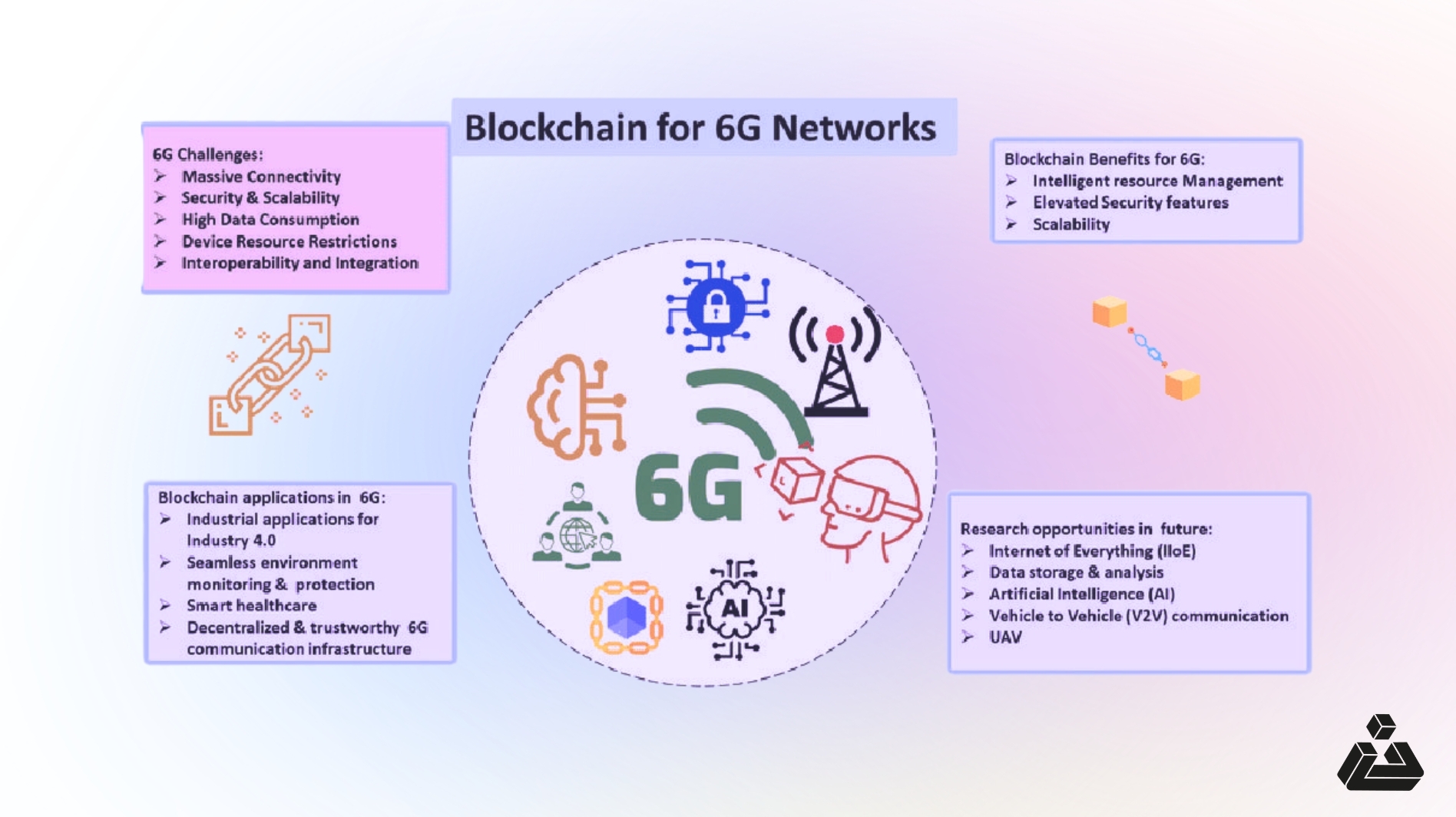
6G Development
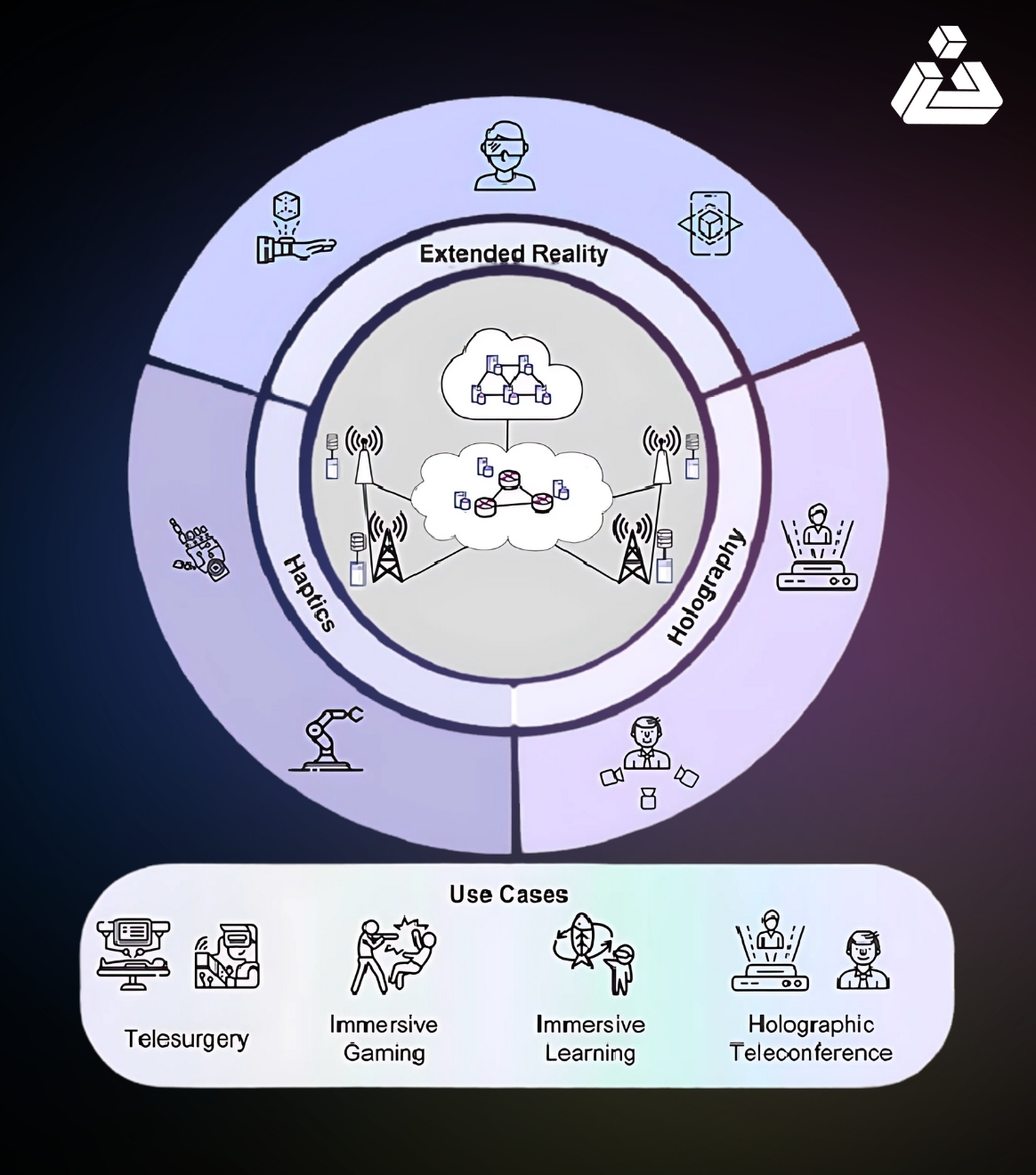
Tada! We have reached the most fascinating and mindblowing part of our article. Nowadays, video calling is very much in demand, and it is working well in 4G and 5G networks. It is a time for 3D calling, virtual reality live streaming, and holographic communication.
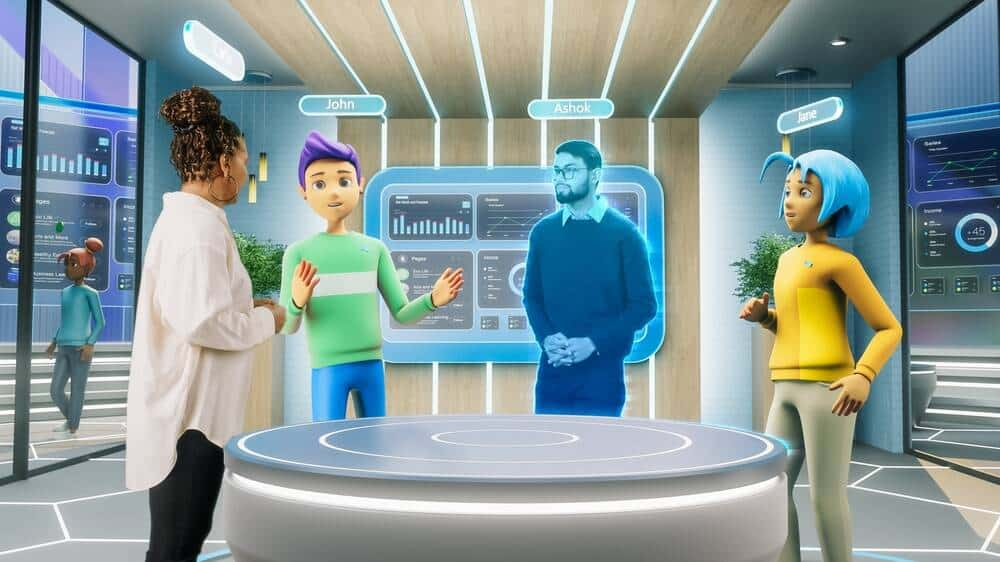

Imagine you’re having a video call with a friend who lives in another country. Instead of just seeing their face on your screen, holographic calling lets you see a three-dimensional, life-like projection of them sitting right in front of you as if they were in the same room.
Blockchain’s role in 6G networks represents a groundbreaking shift in communication technology. By decentralizing data storage and processing, blockchain enhances network efficiency, reduces latency, and bolsters security.
- Decentralized Network Architecture: Blockchain’s integration decentralizes data across the network, improving speed and performance by reducing reliance on central servers.
- Enhancing Security in Communication: Blockchain’s cryptographic features provide robust protection for communication, ensuring that data remains secure and private.
- Smart Contracts in 6G: These automated, self-executing contracts simplify transactions and operations within 6G networks, cutting down on costs and intermediaries while boosting efficiency.
Wrapping up
The fusion of blockchain with telecommunications holds boundless possibilities, often surpassing what the human mind can fully perceive. By integrating blockchain technology into telecom systems, we address multiple challenges while simultaneously ushering in advancements in efficiency, security, and connectivity.
This synergy opens up a new realm of opportunities, highlighting the profound impact blockchain can have on the future of communication. We, BlockApex, are a blockchain consulting company. We are at the forefront of this transformation, exploring and harnessing blockchain’s potential to drive innovation in the telecom sector.
Ready to revolutionize your telecom systems with blockchain? Contact BlockApex today to unlock the future of connectivity.