The types of services from cloud technology, Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Software as a Service (SaaS) and Platform as a Service (PaaS) are quite known. However, Blockchain as a Service (BaaS) is closely related to cloud computing too.
It simply means a third party provides a managed blockchain service in the cloud. Just like how Google Cloud hosts websites, BaaS lets companies use a third-party service to run their blockchain without having to build it themselves.
In this blog we’ll break down the basics of Blockchain as a Service. We’ll cover in detail how it works, and some of its applications. Furthermore, we’ll delve into the challenges, and future of BaaS.
What is BaaS?
According to AWS, “Blockchain as a Service (BaaS) is a managed blockchain service that a third party provides in the cloud. You can develop blockchain applications and digital services while the cloud provider supplies the infrastructure and blockchain building tools. All you have to do is customize existing blockchain technology, which makes blockchain adoption faster and more efficient. “
Hold on, we have a lot to break down in this piece of information, so it goes like:
- Managed Blockchain Service: A third party handles the setup, maintenance, and management of blockchain infrastructure. The service provider ensures that nodes, networks, and security are operational.
- Cloud-Based Provision: The blockchain service is hosted in the cloud, eliminating the need for on-premise servers or infrastructure. Platforms like AWS or Microsoft Azure provide the backbone for hosting blockchain networks.
- Blockchain Applications and Digital Services: You can develop and deploy applications like smart contracts, decentralized apps (DApps), and digital identity systems on top of the provided blockchain infrastructure. Using the service to create a digital voting system or supply chain tracker.
- Cloud Provider Infrastructure: The cloud provider offers the underlying resources—servers, storage, networking, and blockchain tools. The infrastructure includes everything needed to run and scale the blockchain network.
- Blockchain Building Tools: Pre-built tools, APIs, and frameworks provided by the service to make blockchain development easier. Tools for creating tokens, managing identities, or building smart contracts.
- Customization of Blockchain Technology: Users can customize existing blockchain frameworks to suit their needs, rather than building from scratch. Modifying Hyperledger Fabric or Ethereum to create a custom blockchain network.
You can understand these as different working components of BaaS, but before we move onto how it works altogether, let’s view the familiar cloud terms and relation to BaaS in picture and a bit detailed tabular differences.
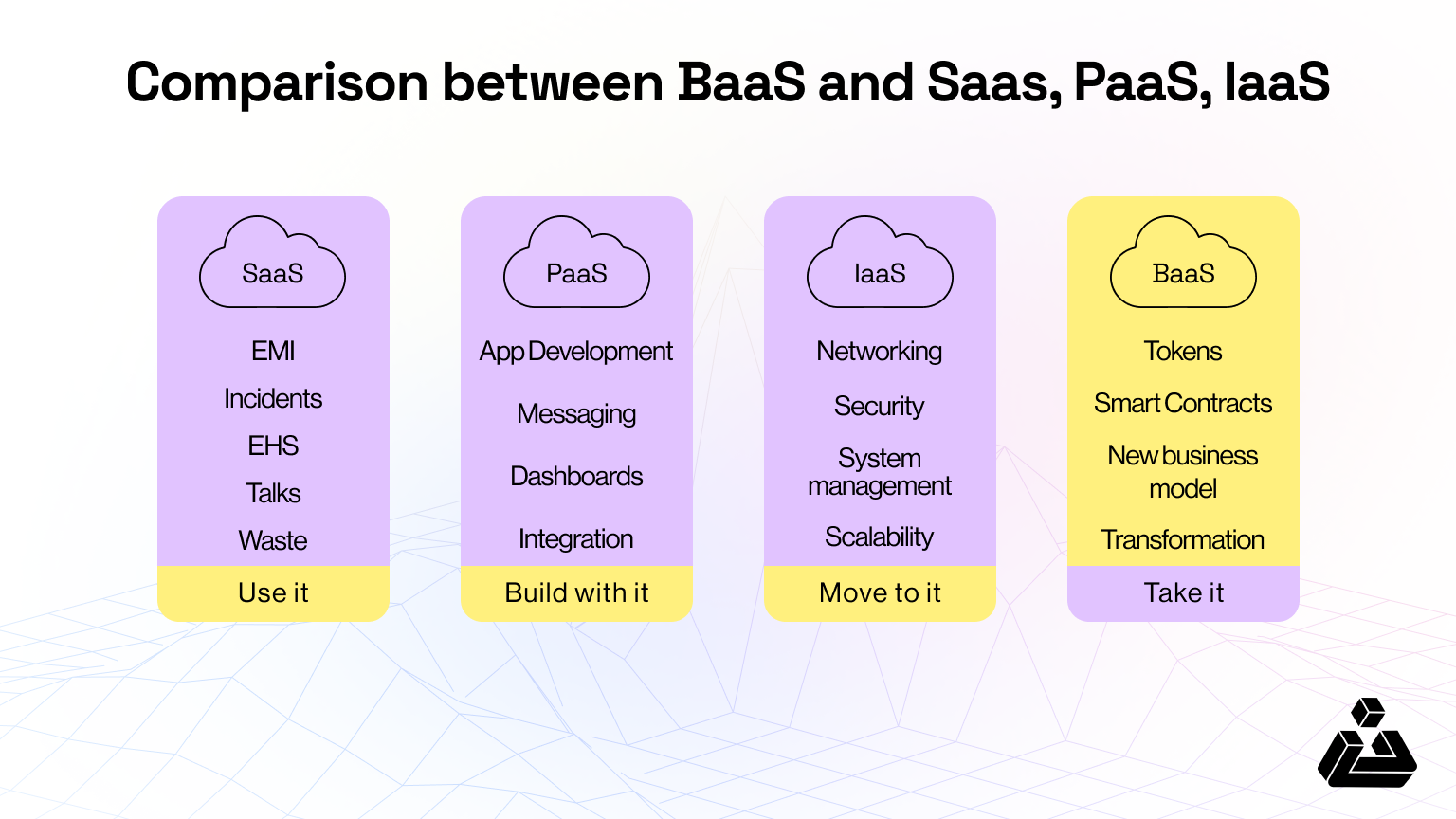
| Feature | IaaS | PaaS | SaaS | BaaS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Provides raw infrastructure. | Offers a platform for development. | Delivers fully functional software. | Offers managed blockchain solutions. |
| Key Offering | Servers, storage, networking. | Development tools and runtime. | User-ready software. | Blockchain infrastructure, tools, and APIs. |
| Who Manages What? | User manages OS and applications. | User develops applications; provider manages infrastructure. | Provider manages everything. | Provider manages blockchain setup; user customizes applications. |
| Relation to BaaS | Hosts blockchain nodes and storage. | Provides blockchain platforms and tools. | Offers user interfaces and APIs. | Combines IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS for blockchain. |
How does BaaS work?
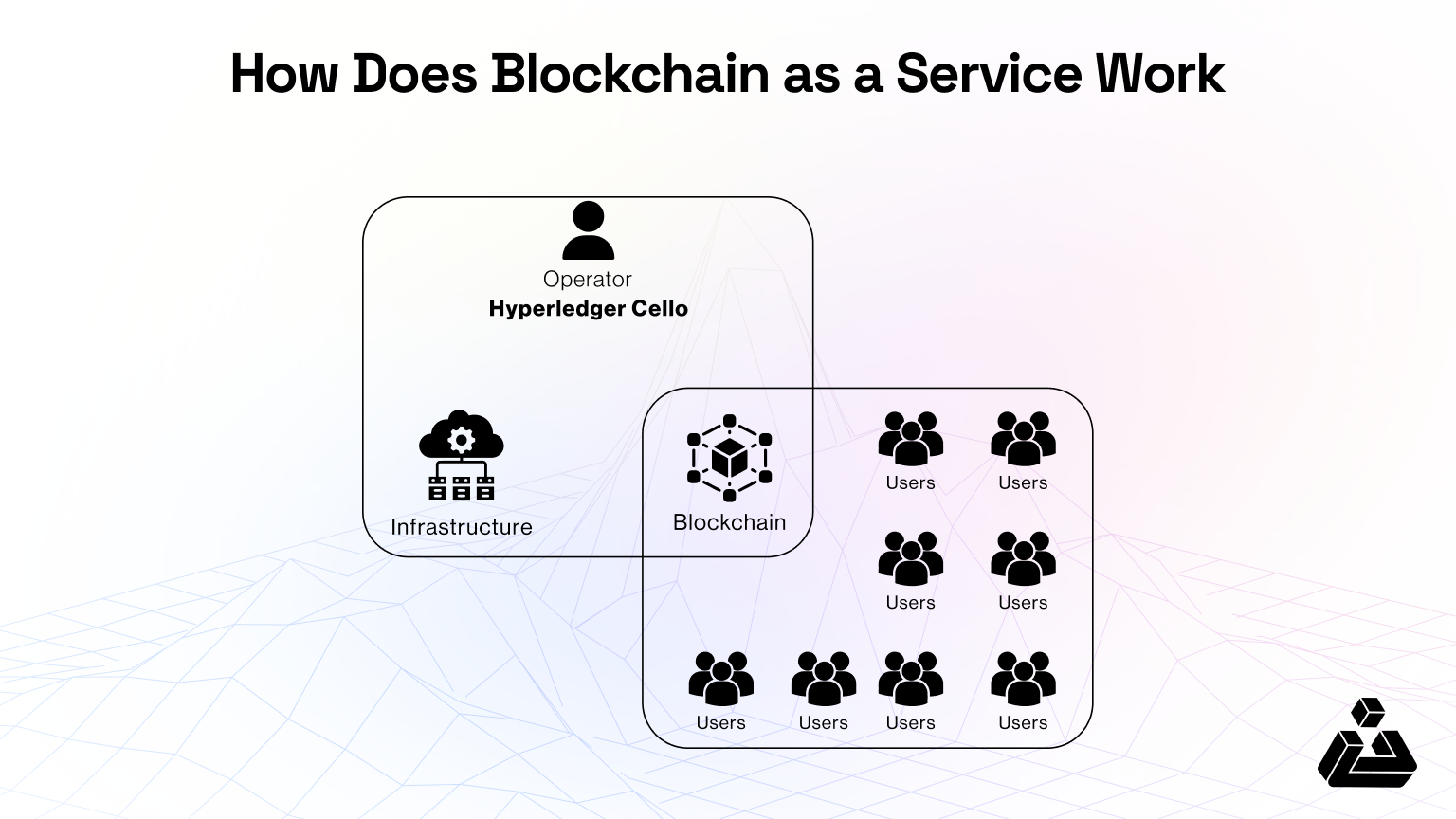
In the graphic above, Hyperledger Cello makes it easier to use blockchain by providing a toolkit that handles all the complicated setup and management. With Cello, businesses don’t need to worry about the technical details of blockchain infrastructure.
It gives users a simple dashboard to deploy and manage their blockchain networks, allowing them to focus on creating applications instead of maintaining the system.
Think of BaaS like a web hosting service for blockchain. Just as a web hosting company takes care of the servers and infrastructure needed for a website, a BaaS provider handles all the backend work for a blockchain.
Users simply build their blockchain applications, while the provider manages the technology, ensuring everything runs smoothly.
However, the services a BaaS provider offers may vary depending on the blockchain framework being used (e.g., Ethereum, Hyperledger, or Corda). For example:
- Ethereum-based BaaS may include support for smart contract deployment.
- Hyperledger-based BaaS focuses on private and permissioned blockchain networks with business-specific use cases
Applications
BaaS is used across various industries to streamline operations without requiring businesses to manage complex blockchain technology.
-
Supply Chain Tracking
BaaS enhances supply chain transparency by tracking goods’ movements through blockchain, ensuring data integrity and regulatory compliance, especially in industries like pharmaceuticals.
IBM Blockchain Platform provides a managed and full stack blockchain-as-a-service (BaaS) offering that allows you to deploy blockchain components on many platforms including open source Kubernetes
IBM Blockchain for Supply Chain helps businesses track goods from production to delivery, ensuring regulatory compliance and transparency.
-
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
BaaS powers DeFi applications for secure financial transactions without banks, fostering decentralized lending, borrowing, and asset management.
Microsoft Azure Marketplace provides different BaaS options to build decentralized finance applications, enabling peer-to-peer lending and asset management on the blockchain.
-
Smart Contracts
Blockchain-based smart contracts automate agreements, reducing costs and increasing transparency, such as in tracking shipments or automating payments in industries like real estate and logistics.
Amazon Managed Blockchain simplifies the deployment of smart contracts and decentralized apps, allowing businesses to automate processes like payments and supply chain tracking.
-
Personal Identity Security
BaaS provides tamper-resistant systems for secure digital identity verification and data sharing, enhancing privacy in sectors like healthcare.
Civic Ledger BaaS offers identity verification systems for businesses to secure users’ digital identities, ensuring privacy while providing full control over their personal data.
-
Intellectual Property Management
BaaS helps protect intellectual property by recording rights on a secure ledger, streamlining licensing, and enabling virtual asset ownership in gaming and NFTs.
-
Digital Voting Systems
BaaS enables the creation of secure and transparent voting systems, enhancing governance in elections and corporate decisions.
-
Audit Capabilities
BaaS provides thorough audit trails, ensuring transparency and compliance by recording blockchain transactions for analysis.
-
Scalability Solutions
BaaS ensures applications can scale to meet growing demand, providing flexible infrastructure to handle increased user activity.
Oracle Blockchain Cloud Service enables scalable blockchain applications, providing businesses with flexible infrastructure that grows with their needs.
-
Blockchain Development Tools & APIs
BaaS providers offer tools, SDKs, and APIs for developers to simplify blockchain app development, including smart contracts, token creation, and data integration.
Azure Blockchain Workbench provides developers with ready-to-use tools to build blockchain applications, including smart contracts and data integration with existing systems.
Clouds of Suspicion: Trust Considerations in BaaS
A fundamental issue lies in the tension between the core principle of decentralized technology, like blockchain, and the reliance on third-party providers for managed blockchain services. Even when entrusted to highly reputable providers, such as Amazon, Oracle, IBM, this approach undermines the very essence of trust mechanisms.
Decentralized ledgers (DLs) remove the need for trusted third parties, offering security, resilience, and data integrity. However, Blockchain-as-a-Service (BaaS) introduces a provider to manage aspects of the DLT infrastructure, potentially re-centralizing certain elements and raising trust concerns.
These issues depend on the service specifics, the risk profile, and the DL’s purpose. Key considerations include:
-
Trust in the Tenant
Tenancy complicates trust in DLT, especially when certain participants control the infrastructure through provider arrangements. This issue varies by context:
- Minimal concern in private blockchains or predefined consortia.
- Significant concern in open environments if infrastructure control is overly centralized.
Multi-party control mechanisms and tooling for decentralized management could mitigate such risks.
-
Trust in the Provider
The trustworthiness of BaaS providers managing DLT infrastructure is critical. While reputable providers invest in security, concerns arise in high-risk environments (e.g., finance, healthcare) or when provider roles include managing nodes, consensus, and identity.
Trust concerns intensify with centralized provider control (SaaS-type services) but reduce in PaaS or federated architectures where tenants have greater control. Enhanced operational visibility, such as validating ledger hashes, can mitigate risks.
Federated architectures, akin to hybrid clouds, distribute components across stakeholders or providers, balancing security, performance, and resilience.
Challenges in implementing BaaS
Whilst there are numerous benefits to using BaaS, such as, it lets businesses skip the technical complexities of blockchain, enabling them to quickly build and deploy solutions without deep expertise. It’s cost-effective and scalable, with businesses only paying for what they use. BaaS simplifies blockchain adoption by eliminating the need for expensive infrastructure and specialized knowledge, allowing businesses to get started faster. This accelerates blockchain’s growth and makes it accessible to companies of all sizes.
The practical implementation of blockchain systems can present a wide range of difficulties. To ensure a successful and long-lasting implementation, businesses using blockchain technology should be mindful of a few key elements and conduct extensive research.
Below are a few points highlighting the implementation challenges:
- Complex and Time-Consuming Development
- Developing blockchain-based applications requires significant time and effort due to the sophisticated nature of blockchain technology.
- Integration with preexisting IT infrastructure demands seamless system and application interoperability.
- Regulatory Uncertainty
- The lack of clear regulations in most jurisdictions poses challenges for both BaaS providers and their clients.
- Compliance requirements vary across industries and regions, complicating adoption.
- Interoperability Issues
- Achieving interoperability between blockchains and other systems is difficult due to differences in architectures, protocols, and standards.
- Cybersecurity Risks
- Despite blockchain’s robust security, BaaS platforms remain vulnerable to cyberattacks and data breaches.
- Social engineering and other indirect attacks can exploit human vulnerabilities and compromise system integrity.
Future of BaaS
The blockchain-as-a-service (BaaS) market has experienced steady growth in recent years and is poised for further expansion as leading organizations increasingly adopt blockchain technologies.
The growing demand for advanced applications across industries such as healthcare, IT and telecommunications, energy and utilities, and retail has significantly driven the adoption of BaaS solutions.
Additionally, investments in research and development are crucial for fostering technological advancements and enhancing the quality of products. As digitalization continues to gain traction and cutting-edge technologies become more integrated, the BaaS market shows immense potential for growth, offering exciting opportunities for innovation and expansion.
Bottom Line
In conclusion, BaaS simplifies blockchain integration, enabling businesses to harness its power without hefty infrastructure costs. BlockApex is dedicated to providing top-tier smart contract services and audits, ensuring security and efficiency for your blockchain projects. Contact us today to elevate your blockchain initiatives.