With the boom of AI, we are already stepping into science fiction, AI Agents are a hot topic in 2025. The AI agents market is projected to grow from USD 5.1 billion in 2024 to USD 47.1 billion by 2030.
The term ‘agents’ has been historically used and in fact, the concept existed since 1993. However, the evolutionary phase has now come into play. AI agents have the ability to perceive, decide and act autonomously, often adapting to changes in the environment.
In this blog, we’ll cover what AI agents are, and how they work. We’ll discuss some real-world examples and the types of AI agents. Lastly, we’ll explore the benefits and drawbacks of AI agents alongside future perspectives.
What are AI agents?
In artificial intelligence, an agent is a computer program or system that is designed to perceive its environment, make decisions, and take actions to achieve a specific goal or set of goals. The agent operates autonomously, meaning it is not directly controlled by a human operator.
Visual assistants, chatbots, Siri, and self-driving cars are a few examples of AI agents.
“Agents are not only going to change how everyone interacts with computers. They’re also going to upend the software industry, bringing about the biggest revolution in computing since we went from typing commands to tapping on icons.” – Bill Gates, Co-founder of Microsoft
“AI agents will become the primary way we interact with computers in the future. They will be able to understand our needs and preferences, and proactively help us with tasks and decision making.” – Satya Nadella, CEO of Microsoft
“By 2024, AI will power 60% of personal device interactions, with Gen Z adopting AI agents as their preferred method of interaction.” – Sundar Pichai, CEO of Google
“AI agents will become our digital assistants, helping us navigate the complexities of the modern world. They will make our lives easier and more efficient.” – Jeff Bezos, Founder and CEO of Amazon
Characteristics of AI agents
These few characteristics of AI agents help us determine and classify if an entity is agentic or not.
- Autonomy: AI agents perform tasks independently without constant human input.
- Perception: They sense and interpret their environment using tools like cameras or microphones.
- Reactivity: They adapt and respond to environmental changes to meet their objectives.
- Decision-making: AI agents analyze data and use algorithms to decide and act effectively.
- Learning: They enhance performance through machine learning, deep learning, or reinforcement techniques.
- Communication: They interact with humans or other agents via natural language, speech recognition, or text exchanges.
- Goal-oriented: Designed to achieve pre-defined or learned goals through interaction and adaptation.
Looking at these characteristics, one may think of ChatGPT as an AI agent but it lacks the power to make autonomous decisions or perceive things at least for now. GPT-5 might also introduce autonomous AI agents that can manage real-world tasks without human intervention.
One example of an AI agent is also a bot who tweets on your behalf; asks GPT to write scripts and posts on your Twitter, quite cryptically, it may also reply to your or other people’s tweets.
How do AI agents work?
An AI system consists of an agent and the environment it interacts with. The agent operates within this environment, which may also include other agents.
An agent can be defined as:
- Perceiving its surroundings through sensors.
- Acting on the environment through actuators.
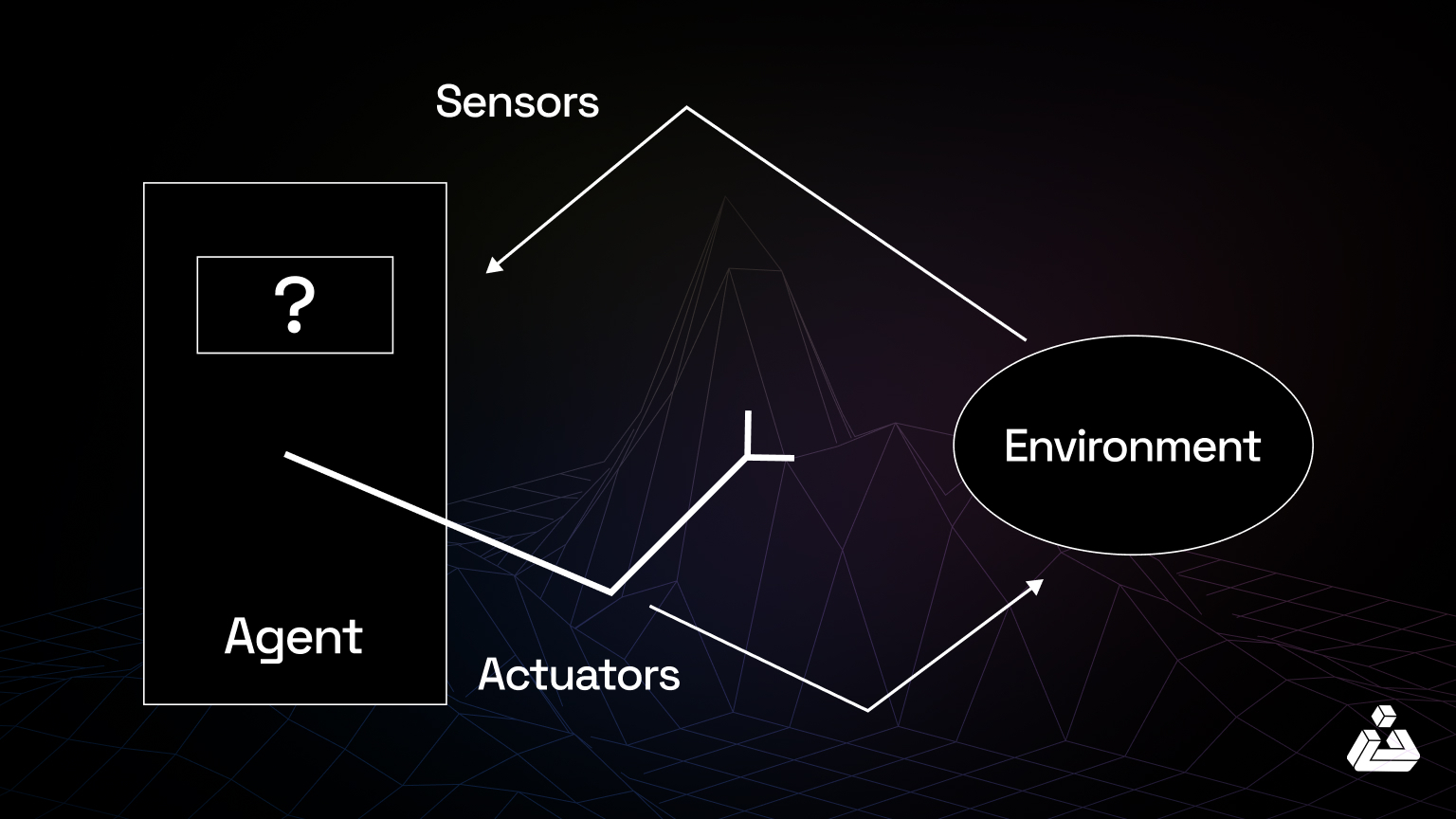
Let’s walk through an example of Alexa, a smart home assistant, to show how AI agents work:
Step 1: Any AI agent first perceives or collects data such as Alexa hearing your voice command using its built-in microphone, such as when you say ‘Alexa, turn off the lights’.
It converts your voice sound into digital data called speech recognition.
Step 2: After understanding the intent behind your request, it’ll start to process the information. It makes use of machine learning algorithms for decision-making.
Alexa will check whether lights are connected to the system and can be turned off remotely so it’ll decide to ‘turn off the lights’. If the command is unclear, Alexa may ask for clarification.
Step 3: Once the decision is made, Alexa sends a command to the smart light bulbs in your home (via a smart home hub or direct Wi-Fi connection).
The action is executed by turning off the lights.
Step 4: AI agents learn and adapt quickly and update their language model based on feedback, such as recognizing different accents or language variations over time.
Alexa may notice that you often turn off the lights at a specific time every evening, so it might suggest automating the process through a routine.
Types of AI agents
Here are some main types of AI agents along with some real world examples.
-
Simple Reflex Agents
Operate based on straightforward condition-action rules, responding to current inputs without memory of past events.
Example: A thermostat that activates the air conditioner when the temperature exceeds a set limit.
-
Model-Based Reflex Agents
Use internal models of the environment to track changes and consider historical percepts for more informed decisions.
Example: A chess-playing AI that factors in previous moves and the current board setup to plan its strategy.
-
Learning Agents
Adapt and improve performance by learning from experiences, and incorporating machine learning techniques to refine behavior.
Example: A spam filter that adjusts to detect new spam types based on user feedback.
-
Utility-Based Agents
Make decisions by evaluating the desirability of outcomes through a utility function, aiming to maximize performance.
Example: An investment advisor AI that analyzes potential returns and risks to recommend optimal investments.
-
Hierarchical Agents
Divide tasks into levels, with high-level agents managing broader goals and lower-level agents handling specific tasks.
Example: A manufacturing agent system where a main agent oversees production, while others control individual machines.
-
Virtual Assistants
Use natural language processing and machine learning to understand and interact with humans intelligently.
Example: Google Assistant, which processes commands, provides information, and learns user preferences.
-
Robotic Agents
Navigate and interact with physical environments autonomously using sensors, decision-making algorithms, and models.
Example: A self-driving car that detects obstacles and follows traffic rules to navigate safely.
Benefits of AI agents
AI agents enhance customer experience and facilitate smoother business operations.
-
Enhanced Productivity
AI agents are autonomous systems designed to execute specific tasks independently. By delegating repetitive or routine activities to these agents, organizations can streamline operations and free up their teams to focus on high-priority, creative, or strategic initiatives, ultimately adding greater value to the business.
-
Cost Optimization
Intelligent agents minimize costs associated with inefficiencies, human errors, and labor-intensive processes. They reliably handle complex operations by following adaptive, consistent models that adjust to changing conditions, reducing waste and enhancing overall efficiency.
-
Smarter Decision-Making
AI agents leverage machine learning (ML) to process vast amounts of real-time data, enabling informed and timely decisions. For example, businesses can deploy these agents to analyze market trends and product demand during campaigns, offering insights that drive better strategies and outcomes.
-
Elevated Customer Experience
Modern customers expect personalized, responsive interactions. AI agents help businesses deliver by offering tailored product recommendations, instant support, and innovative engagement methods. These capabilities improve customer satisfaction, loyalty, and conversion rates, enhancing long-term relationships.
Real-world examples of AI agents in different industries
Companies like Amazon, and Netflix are relying heavily on AI agents for automation and elevating customer experience. Amazon GO introduced the concept of a cashless store, grab and walk away on the go. They use a mix of sensors, deep learning, and AI agents to restock shelves and understand human behavior and preferences.
Different industries are adopting this technology, and it’s paving the way for Web3, metaverse, IOT, and blockchain. Some examples are already implemented and some are being worked upon.
Blockchain
- Automated Trading: AI agents monitor markets, execute trades in real-time, and optimize portfolio performance faster than humans. For instance, they maximize yield in liquidity pools like Balancer.
- Risk Management: They identify vulnerabilities in smart contracts or portfolios, helping users mitigate losses and enhance security.
- NFTs and Generative Art: AI agents create interactive NFTs (iNFTs) with evolving traits. Tools like Binance’s Bixel enable AI-generated art directly minted on blockchains.
- Simplifying Blockchain Use: AI agents automate wallet management, transaction approvals, and DAO activities (e.g., voting or strategy proposals), making crypto more user-friendly.
- Payments: They facilitate crypto micropayments for pay-per-request services (e.g., weather data) and manage seamless transfers autonomously.
IoT
- Autonomous Cars: Google’s driverless car uses sensors to collect environmental data and makes decisions in real-time, handling unpredictable situations autonomously.
- Virtual Assistants: Siri, and Bixby process user and environmental data to assist decision-making, providing personalized support.
- Home Automation: AI agents like Amazon Alexa and Google Nest automate household tasks and improve energy efficiency.
Fintech
- Fraud Detection: AI agents in systems like Sift identify suspicious patterns in financial transactions.
- Customer Service: Virtual assistants in banking apps streamline user queries and provide instant support.
Future of AI Agents
Imagine entering a metaverse where every aspect, from the environment to NPC (Non-Player character) behavior, changes dynamically to suit your mood, history, and desires. These AI-driven environments could use advanced data analytics and emotional recognition to create truly immersive, bespoke experiences.
AI agents can do more than a human mind can fathom, AI can be scary as it keeps learning from its experiences and adapts quickly. It can retain memory of past user interactions and its dataset keeps growing exponentially making it a powerful beast.
Leading experts, such as Elon Musk and Stephen Hawking, have frequently warned about the existential threat posed by AI if not properly controlled. Musk, for example, has likened AI to “summoning the demon” and argued that a superintelligent AI could pose a significant risk to humanity if its goals diverge from human values.
Hawking similarly expressed concern that advanced AI could “develop a will of its own” and could outpace human intelligence in ways that might be difficult to control.
Conclusion
AI agents can facilitate humans from their daily house chores to office tasks and even so more. Various organizations are rooting for human-centered AI. This approach focuses on making sure AI systems are transparent, interpretable, and accountable to people.
Ethical frameworks need to be designed in order to practice the development of AI with caution and awareness. Only time will truly reveal if the benefits will outweigh the potential drawbacks.
At BlockApex, we’re committed to exploring and implementing cutting-edge AI solutions tailored to your needs. Want to see how AI agents can revolutionize your operations? Let’s innovate together—reach out to BlockApex today!