ADOT Finance integrates a blockchain-based marketplace and bridging system that facilitates the exchange and creation of digital assets across different blockchain environments. It offers specialized platforms for NFT and token transactions, focusing on security, efficiency, and user empowerment through innovative trading and bridging mechanisms.
Vision and Mission:
ADOT Finance aims to enhance the interoperability and usability of digital asset exchanges, ensuring a seamless and secure environment for both NFT and token transactions across various blockchain platforms. The mission is to redefine the user experience within the DeFi landscape by introducing a bridge and marketplace that not only supports robust cross-chain interactions but also ensures high security and operational excellence in token and NFT transactions.
Audit Focus:
Our comprehensive audit targeted the core components of ADOT Finance: the Bridge and NFT Marketplace modules. Key areas scrutinized included:
- Security protocols and validation processes for cross-chain transactions.
- Smart contract logic and compliance with security best practices in marketplace operations.
- Efficiency and integrity of bridging operations.
- Ensuring the security and efficiency of cross-chain transactions.
- Evaluating the smart contract logic against industry best practices.
- Examining the integrity and performance of the bridging operations.
- Investigating the marketplace’s adherence to NFT standards and trading security.
Audit Findings:
BlockApex’s comprehensive audit uncovered several vulnerabilities in the ADOT Finance. The ADOT team responded swiftly and effectively, addressing and resolving the issues in a timely manner. Their proactive approach and quick mitigation of risks demonstrate a strong commitment to prioritizing security and ensuring the integrity of the protocol.
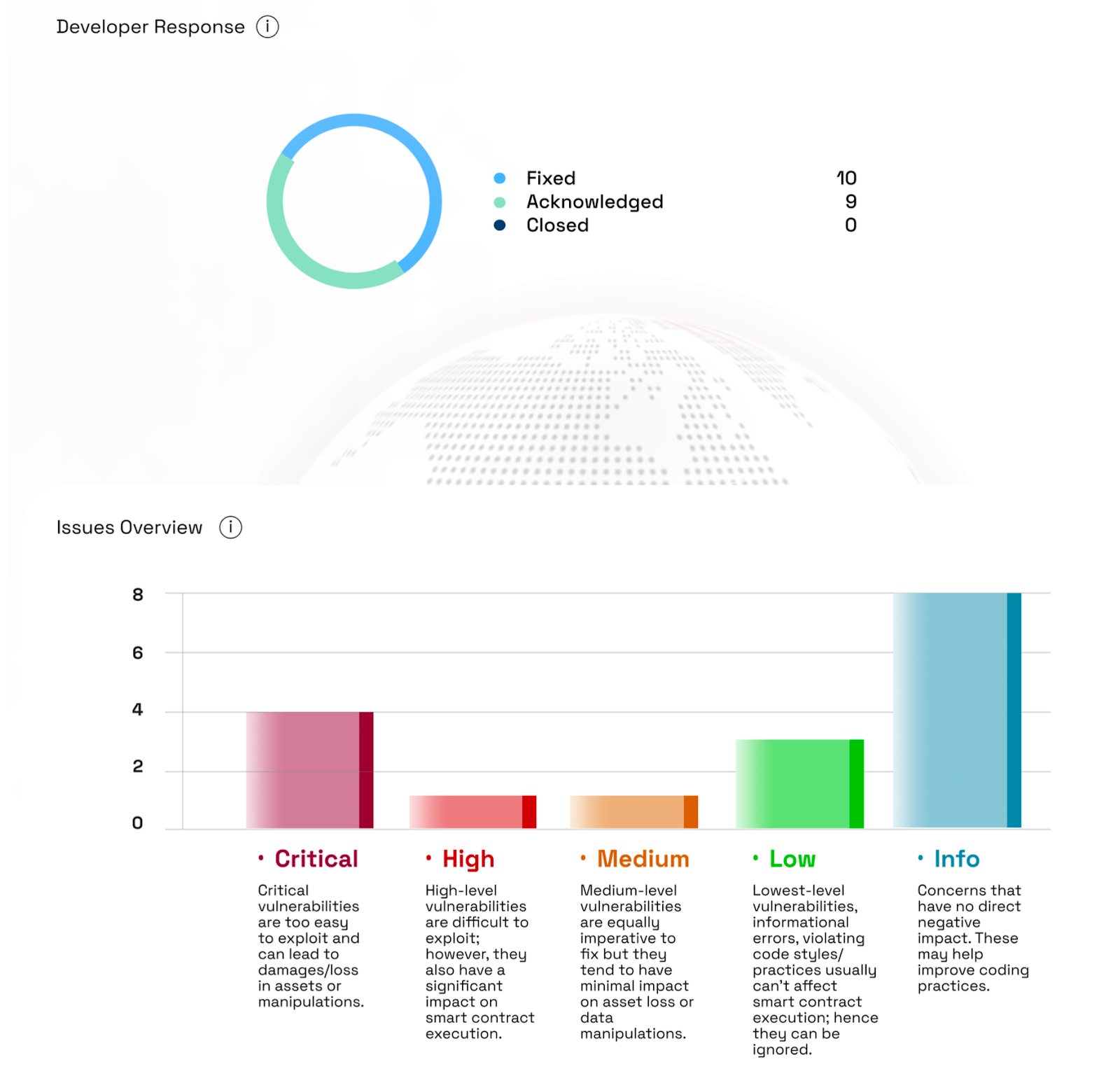
Key Findings:
Reentrancy Vulnerability:
This was found in the ListingEnglishAuction.sol contract. The vulnerability arises because state updates occur after external calls, allowing an attacker to make repeated calls and drain funds.
Token Compatibility Issues:
The auction system couldn’t handle ERC20 tokens like USDT that don’t return a boolean value from transfer functions, leading to auctions being frozen.
Front-Running Exploit:
This occurs in the CollectionOffer.sol contract. Bidders could change their offer price just before an offer is finalized, reducing the amount the seller receives.
Unvetted Tokens:
The bridge mishandles tokens with special mechanics like rebasing or FeeOnTransfer, leading to potential discrepancies in token amounts and unexpected fees.
Spamming Risk:
Due to lack of checks against duplicate listings by a single user in the listingspot.sol contract, sellers could flood the marketplace with many listings of the same NFT at different prices.
Data Deletion Errors:
In AdotKeeper, incorrect data deletion occurred because the wrong mapping was targeted, affecting the integrity of data handling within the contract.
Missing Events in Multisig:
The multisignature contract lacked event emitters for adding or removing members, which is crucial for auditability and tracking changes in contract states.
Listing Start Time Validation:
Listings could be activated with start times set in the past, allowing them to commence and progress without synchronization with real time.
Exclusion of Zero ID NFTs:
The marketplace contracts incorrectly excluded NFTs with a token ID of zero due to a validation rule, which is not compliant with ERC-721 standards.
Inefficient Gas Usage:
Using postfix incrementation (i++) in loops was less gas-efficient compared to prefix (++i), resulting in higher costs for transactions.
Recommendations:
Implement Reentrancy Guards:
Apply OpenZeppelin’s ReentrancyGuard to secure contracts from potential reentrancy attacks, significantly bolstering security during transactions.
Adopt SafeERC20 Library:
Integrate the SafeERC20 library across all ERC20 token interactions to ensure compatibility and prevent transaction failures, enhancing reliability.
Enhance Validation Mechanisms:
Establish stringent checks for bid and offer updates to prevent malicious front-running and ensure the integrity of transactions across the platform.
Develop Token Whitelisting Protocols:
Create a rigorous vetting process for all tokens, especially those with unique features like rebasing and FeeOnTransfer, before allowing them into the ecosystem.
Prevent Duplicate Listings:
Implement validation to detect and stop duplicate NFT listings by the same user to preserve marketplace integrity and user experience.
Institute Time Validation Checks:
Adjust system logic to disallow listings from starting in the past, ensuring all auctions and sales commence at or after the current block timestamp for fairness.
Key Takeaways for Multichain NFT Bridge Auditing
Non-standard Token Transfer Logic:
This involves the mechanisms for transferring NFTs between blockchains, where errors can lead to lost or duplicated assets.
Smart Contract Interactions:
The interaction between contracts, especially when invoking contracts on another blockchain, where issues can arise from inconsistent state or failed transactions.
Insufficient Authentication and Authorization:
Ensuring only authorized transactions are processed, particularly in permissioned actions like asset transfers.
Mishandling of External Calls:
Calls to external contracts or oracles that provide cross-chain data are critical and can be manipulated or spoofed.
Locking and Unlocking of Assets (Vaults):
These are the safes where assets are kept during the transfer. If their security isn’t tight, someone could break in and steal the assets, or they could be locked up forever by mistake, making them inaccessible.
Oracles:
These provide external data needed to make decisions on the bridge, like currency exchange rates. If this data is wrong—either by mistake or manipulation—the decisions made based on it can lead to wrong asset valuations or incorrect transaction executions.
Auditor’s Verdict:
BlockApex’s thorough audit showcases ADOT Finance’s strong commitment to security and progressive technology within the blockchain space. The proactive response to the audit findings highlights ADOT Finance’s dedication to evolve and enhance their system.
Future Implications:
The successful enhancements resulting from the audit subtly strengthen ADOT Finance’s security architecture. This positions the platform as a prudent choice in the decentralized finance space, suggesting a trajectory towards steady and sustainable innovation.
Conclusion:
ADOT Finance carves a niche in the decentralized finance space by seamlessly integrating advanced NFT and token bridge functionalities with enhanced security protocols. Meticulous design, and active improvements underscore ADOT’s commitment to maintaining a secure and user-centric platform. This positions ADOT as a forward-thinking in facilitating very efficient digital asset exchanges, continually adapting to the evolving needs of the DeFi community.