Bitcoin Layer-2 networks offer a much-needed answer as Bitcoin’s rapid growth increases the demand for scalable solutions. With transaction speed slowed and fees surging, user frustration has grown. Bitcoin Layer-2 protocols, built on top of the Bitcoin blockchain, enable faster, lower-cost transactions by processing them off-chain. As a result, they reduce congestion and improve overall efficiency. In this article we will zoom in on some of the most promising Bitcoin Layer 2 projects, exploring how they are addressing scalability concerns of the Bitcoin network.
What is Bitcoin Layer 2?
Layer 2, or L2, refers to a secondary framework or protocol that is built on top of an existing Layer 1 blockchain. The primary purpose of the L2 solution is to enhance scalability, cost efficiency, security, and finality.
As we discussed what L2s are, their main purpose is to improve the scalability and efficiency of the Bitcoin network. Let’s see how they work.
A blockchain network is made up of two interconnected layers – the execution layer and the consensus layer. Bitcoin L2 solutions create an off-chain execution layer to process transactions and advanced operations like smart contracts efficiently.
Once transactions are processed off-chain, their details are readied for final submission to the Bitcoin blockchain. These details are carried forward to the consensus layer for final validation and settlement by miners or validators. The main network’s security is maintained through final settlement on-chain.
Bitcoin Layers 2s vs Ethereum Layers 2s
Bitcoin L2s are becoming prominent but Ethereum L2s are relatively popular. One main reason is that Ethereum’s smart contract supports contemporary applications like DeFi, and NFT but Bitcoin does not have the same applications. Here is the simplest breakdown of this comparison.
|
Aspect |
Bitcoin Layer-2s |
Ethereum Layer-2s |
|
Blockchain |
Bitcoin | Ethereum |
|
Main Goal |
Scale throughput, reduce costs, and add programmability (including application support) | Scale speed, reduce costs |
|
Settlement Layer |
Bitcoin blockchain | Ethereum blockchain |
|
Dominant Types |
State channels, sidechains | Sidechains, rollups |
|
Virtual Machine |
Developing execution layers with virtual machine capabilities (similar to EVM) | Directly uses Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) |
|
Layer-2 Projects |
Enhancing Bitcoin’s transaction throughput and supporting applications | Primarily focused on scaling network efficiency |
|
Smart Contracts |
Indirect support via virtual machine-like layers | Direct support through EVM |
|
Use Cases |
Limited compared to Ethereum | Supports DeFi, NFTs, and a wide range of blockchain applications |
Top Bitcoin Layer 2 Projects
01- Lightning Network
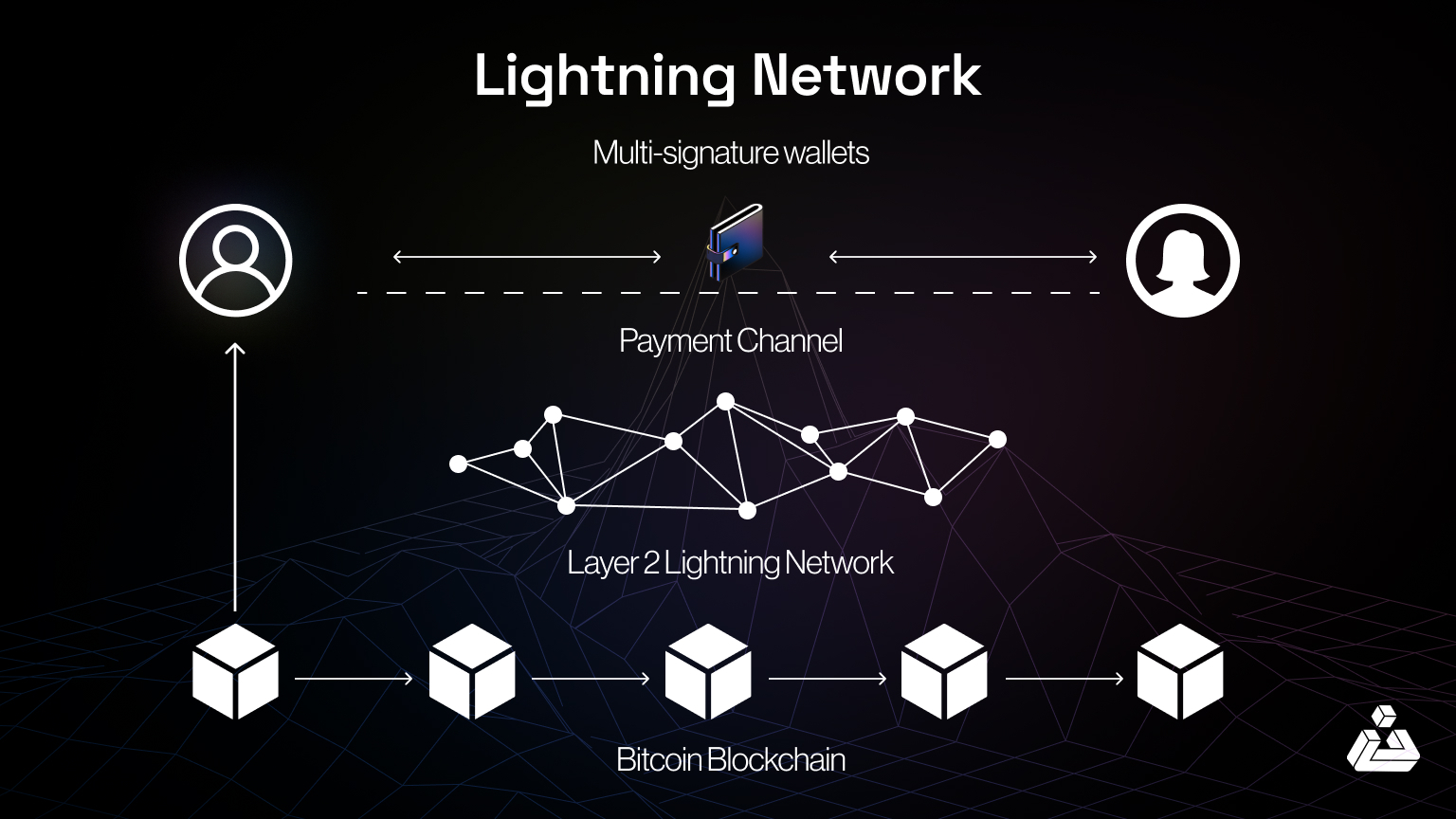
- Year of Launch: The concept was first proposed in a white paper in 2015, and the network started becoming operational around 2018.
- Lightning Network TVL: $323.09 million
The Lightning Network (LN) is a Layer 2 payment protocol built on the Bitcoin blockchain to enable fast, low-cost transactions by processing them off-chain. By using payment channels, LN addresses scalability issues, recording only the opening and closing balances on the blockchain.
Since its 2018 launch, LN has introduced features like Keysend and Wumbo Channels, expanding its transaction capabilities. With support from figures like Jack Dorsey and integration into platforms like Twitter, LN continues to grow capable of handling up to 1 million transactions per second (TPS) theoretically, compared to Bitcoin’s main blockchain, which has a throughput of around 7-10 TPS, boosting Bitcoin’s use as a peer to peer electronic cash system.
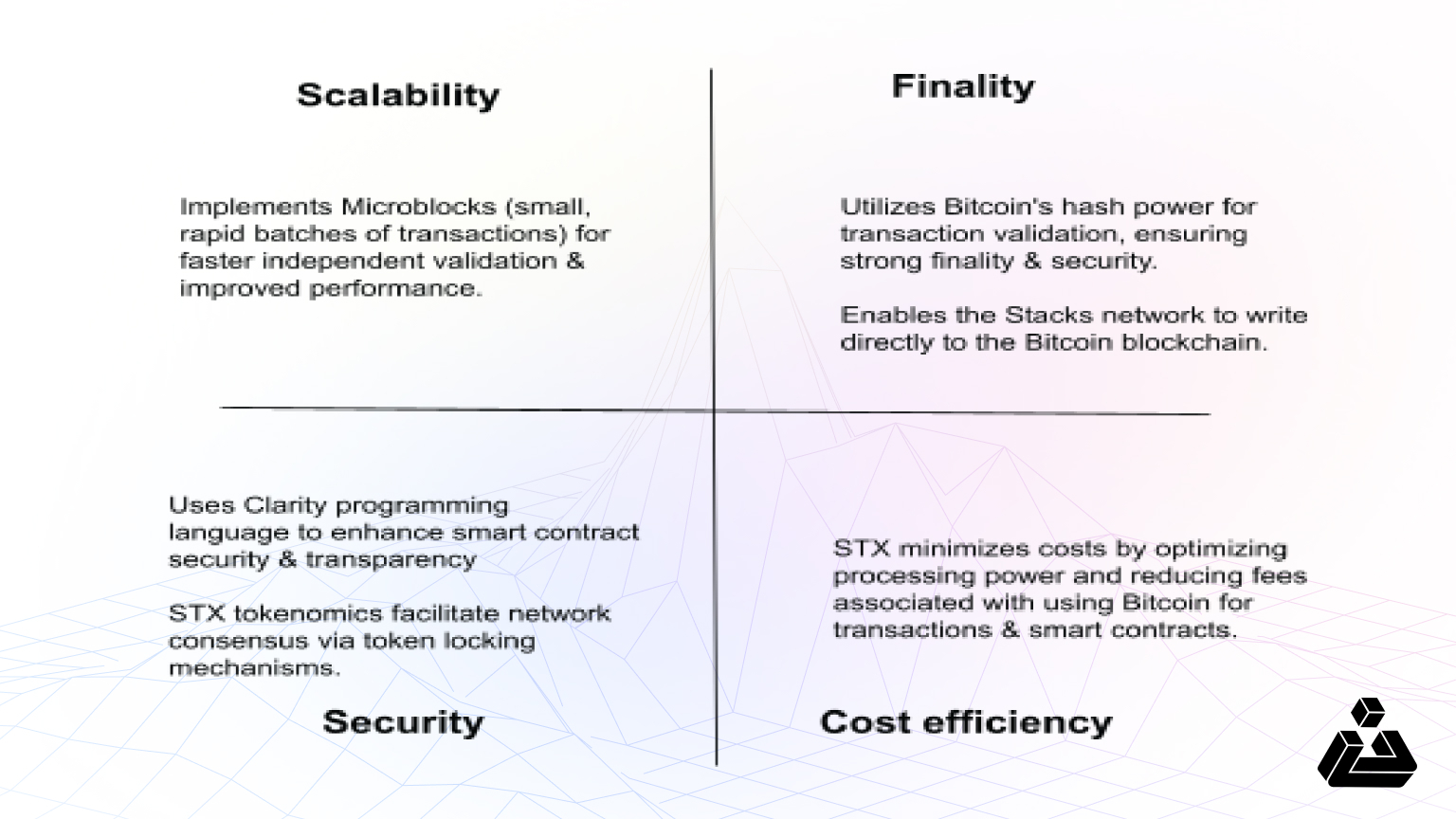
We have summarized the key takeaways with four crucial aspects present in every L2: Scalability, Security, Finality, and Cost efficiency
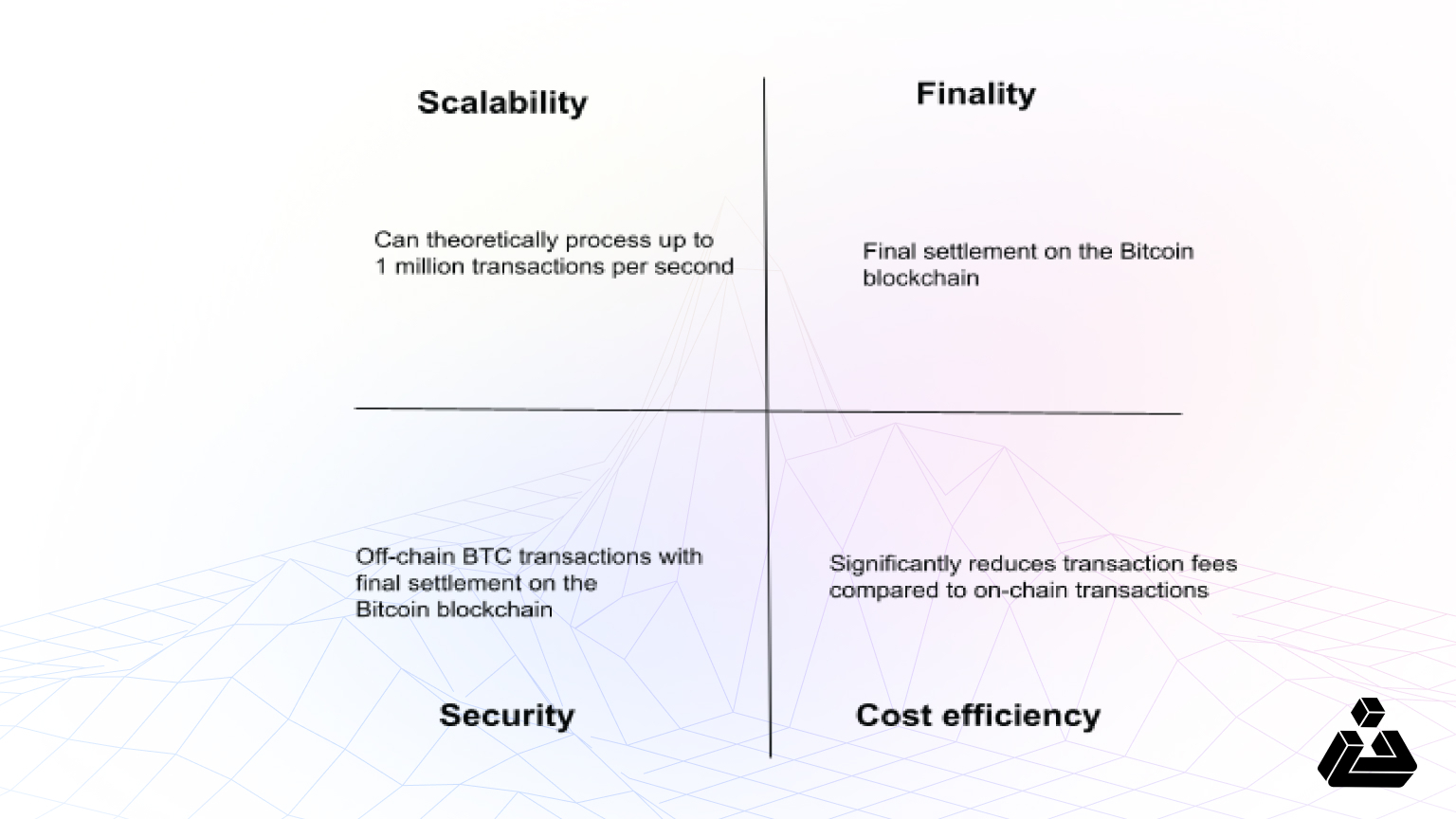
Additional features:
- Transactions are nearly instantaneous.
- Enhanced features like Wumbo Channels (allowing users to create larger payment channels than the standard limit) and Keysend (facilitating spontaneous, trustless payments over the Lightning Network) improve capacity and functionality.
02- Rootstock
- Year of Launch: Rootstock (RSK) was launched in 2018.
- Rootstock TVL: $167 million+

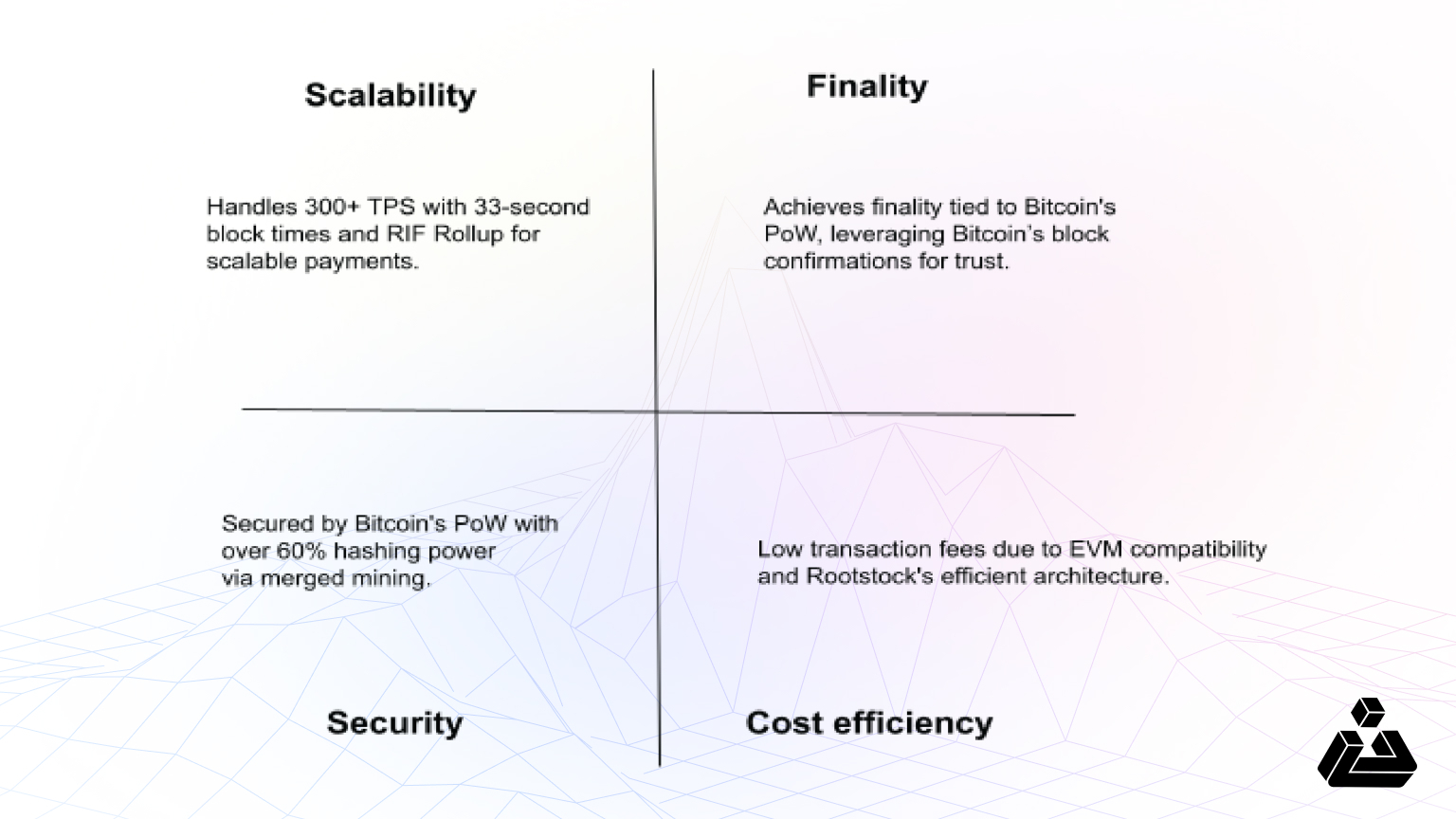
Rootstock is the first, longest-lasting, and biggest Bitcoin sidechain. It is the only Bitcoin layer 2 that combines the security of Bitcoin’s proof-of-work, with Ethereum’s smart contract capabilities.
Secured by 60% of Bitcoin’s hashing power, it uses a trustless two-way peg to convert Bitcoin (BTC) into RBTC for smart contract and dApp interaction. Rootstock supports over 120 Web3 apps and tools, offering EVM compatibility, low fees, and fast transactions (300+ TPS).
Merged Mining allows Bitcoin miners to validate both Bitcoin and Rootstock blocks simultaneously, enhancing security while earning RBTC rewards for securing both networks.
03- Merlin
- Year of Launch: February 2024
- Merlin TVL: $148.05m
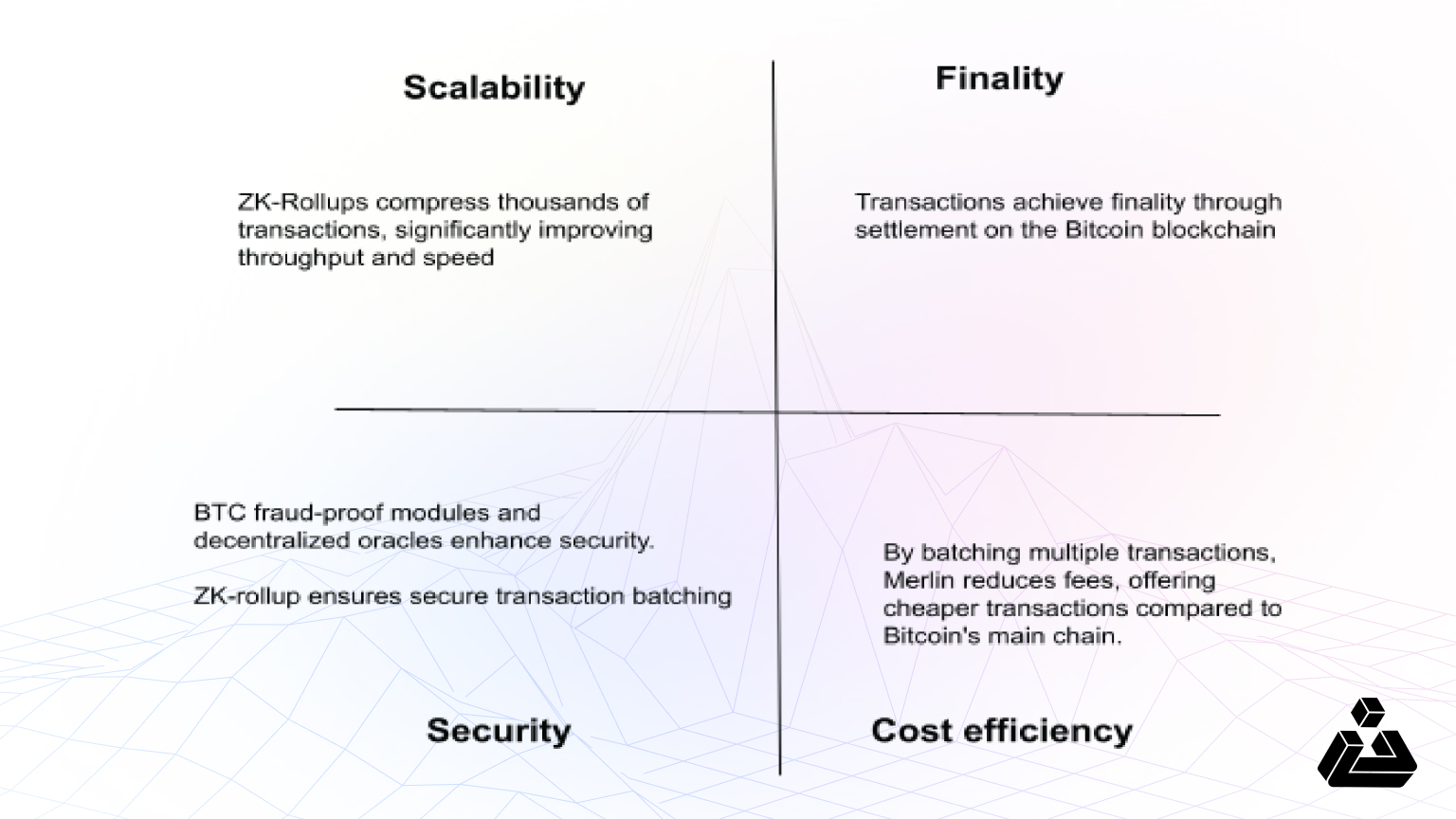
Merlin Chain, launched in February 2024, has quickly distinguished itself in the competitive landscape of Bitcoin-native projects. As an EVM-compatible Layer 2 rollup network, it allows users to access the platform via their Bitcoin wallets through BTC Connect.
By employing zero-knowledge rollups, Merlin batches transactions for efficient settlement on the Bitcoin blockchain, significantly improving speed and reducing costs while maintaining high security. Its compatibility with Ethereum protocols also enables developers to easily deploy existing applications without major modifications.
04- Stacks
- Year of Launch: Originally known as Blockstack, the project rebranded to Stacks in 2020.
- Stacks TVL: $94.13m million
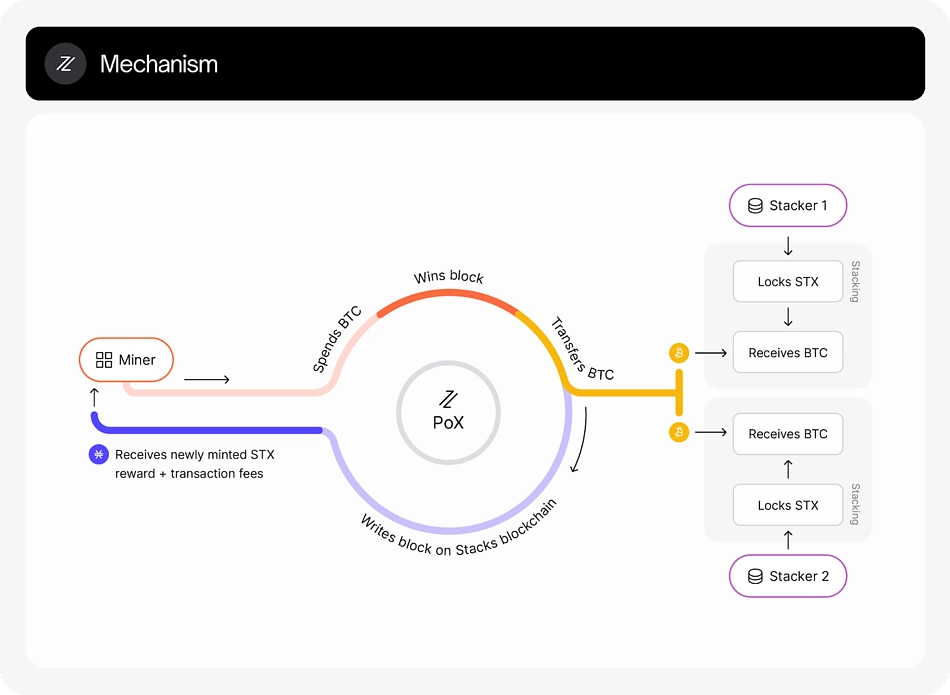
Stacks operates as a Bitcoin Layer 2 by leveraging Bitcoin’s security and finality, utilizing Bitcoin’s hash power for transaction validation. It simplifies the relationship between Layer 1 and Layer 2 by allowing all data and transactions on Stacks to be hashed and permanently stored on Bitcoin L1, ensuring verifiability.
With the upcoming sBTC, Stacks aims to facilitate a decentralized peg to Bitcoin, making BTC the primary unit of the economy. Additionally, Stacks contracts can directly interact with Bitcoin transactions, enabling seamless asset transfers and enhancing the ecosystem’s functionality.Stacks hosts a wide range of applications, including DeFi platforms (e.g., Alex, Arkadiko), NFTs, and decentralized blogging (e.g., Sigle).
Consensus mechanisms help decentralized networks agree on transaction integrity. As depicted in the image above, Stacks uses the Proof of Transfer (PoX) consensus, which combines elements of Proof of Stake and Proof of Burn. PoX connects miners on the Bitcoin blockchain with stackers/stakers on the Stacks network.
Conclusion
Bitcoin Layer-2 solutions are crucial for the evolution of the Bitcoin ecosystem. They tackle significant challenges while unlocking new opportunities for Bitcoin’s broader adoption, representing important advancements toward a scalable and efficient blockchain environment. In this context, BlockApex is making valuable contributions by developing secure solutions and conducting thorough audits. Reach out to us today to learn how we can support your journey in this innovative landscape.