Smart contracts may be an oxymoron and are not necessarily ‘smart’. Their functionality depends entirely on the quality of the data they receive and the code that governs them. Like a smartphone or smart TV, which simplifies tasks but is not really ‘intelligent’, these contracts automate transactions based on predefined rules.
Their effectiveness depends on accurate input and well-embedded logic, making them efficient but neither adaptive nor capable of independent thought. Artificial intelligence or Machine learning-based systems like autonomous vehicles can be called truly ‘smart’ as they have the ability to analyze patterns and make decisions.
Nevertheless, smart contracts being self-executing agreements have demonstrated powerful functionality, particularly in streamlining transactions and managing cash flow. This article explores the concept of “Smart Contract Cash Flow,” diving into what smart contracts are, their use cases, benefits, challenges, real-world examples, comparison with traditional systems, and future prospects.
What is a smart contract and some of its characteristics?
“A smart contract is a mechanism involving digital assets and two or more parties, where some or all of the parties put assets in, and assets are automatically redistributed among those parties according to a formula based on certain data that is not known at the time the contract is initiated.” -Vitalik Buterin
This quote effectively captures the essence of smart contracts as self-executing agreements that automate the management of digital assets including crypto, tokens, collectibles, or digital real estate without requiring human intervention. Redistribution occurs among multiple parties as part of a collaborative agreement, eliminating intermediaries and relying on predefined conditions.
Some unique characteristics of smart contracts are:
- Smart contracts are machine-readable code run on a blockchain platform
- Smart contracts are part of one application program
- Smart contracts are event-driven program
- Smart contracts are autonomous once created no need to monitor
- Smart contracts are distributed
What is smart contract cash flow?
Smart contract cash flow refers to the movement of funds within a smart contract, a self-executing digital agreement that enforces its terms automatically when predefined conditions are fulfilled. These contracts use cryptocurrencies or tokens to transfer value, ensuring a seamless, transparent, and automated cash flow process.
Benefits of smart contract cash flow
Suppose you want to sell your house or rent your apartment to someone, then you can simply deploy a smart contract in an existing blockchain network. Information about the property can be securely stored on the blockchain, allowing anyone on the network to access it, but without the ability to modify it, adding transparency.
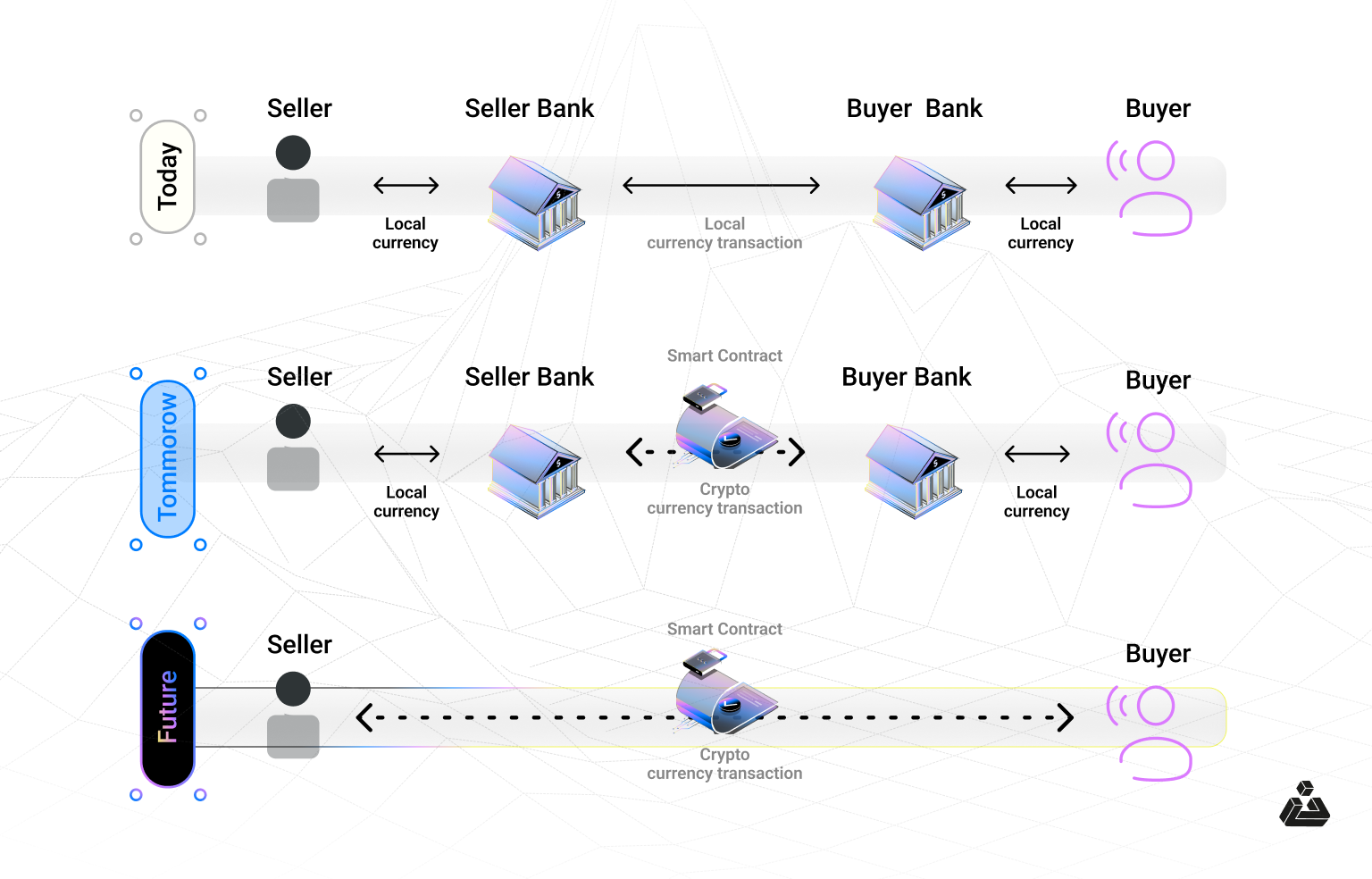
This enables you to find a buyer for your property without relying on third parties. Using this example, blockchain-based smart contracts offer several advantages, including:
-
Speed and real-time updates:
The contract executes instantly when conditions are met, such as payment or lease confirmation.
-
Transparency & Accuracy:
Blockchain’s open ledger ensures the visibility of transactions. The terms are clear and pre-defined in the code, reducing the chances of error in execution.
-
Lower execution risk & security:
Transactions only proceed when all conditions are met, minimizing the risk of fraud and disputes.
-
Fewer intermediaries:
No need for agents or brokers, as the blockchain handles the transaction.
-
Lower cost:
Without intermediaries, you save on commission fees.
-
Trustlessness:
No need for trust between parties like traditional platforms or agencies. as the code enforces terms.
Also Read: Top 10 Smart Contract Vulnerabilities List
Smart contract use-cases & Real world examples
Let’s have a look at some industrial smart contract use cases and real-world examples.
-
Supply chain:
Smart contracts improve transparency and efficiency by automating the verification of terms at each stage of the supply chain, facilitating real-time cash-flow tracking, and ensuring trust without the need for intermediaries.
IBM’s Food Trust platform is a blockchain-based supply chain solution that tracks food products from farm to table. It uses smart contracts to ensure the authenticity of supply chain data, reducing fraud and inefficiencies.
-
Healthcare:
Smart contracts can securely store and manage patient data, streamlining processes like billing or cash flow management, claims or even issuing medication. They protect patients’ confidential data ensuring quick and transparent actions.
MedRec, is a blockchain-based medical system, that uses smart contracts to manage medical records and provide real-time updates. It ensures that only authorized users can access the records, improving data privacy and interoperability.
-
Real estate:
In real estate, smart contracts simplify property transactions by automating tasks like property transfer, escrow management, and document verification.
Propy is a blockchain-based real estate platform that uses smart contracts to automate property sales, title transfers and digital signatures. It has been implemented in various countries, reducing paperwork and intermediaries.
Also Read: How Smart Contacts are Disrupting Real Estate Sector?
-
Decentralized Finance:
Platforms like Aave and Compound use smart contracts to enable decentralized lending and borrowing. Users can lend their crypto to earn interest or borrow against their holdings without needing traditional banks.
The terms such as interests, and collateral, are managed automatically by smart contracts, ensuring transparency and efficiency.
-
Trading:
Smart contracts power decentralized exchanges (DEXs), allowing users to trade digital assets without intermediaries. These contracts handle all trade execution and settlement processes.
Uniswap and SushiSwap are decentralized exchanges that allow peer-to-peer trading of tokens using smart contracts. These contracts automatically execute trades based on predefined conditions, making the process secure and decentralized.
-
Governance:
Smart contracts are used for decentralized governance where stakeholders vote on proposals, and the execution of decisions is automated.
MakerDAO, which manages the DAI stablecoin, uses smart contracts to allow token holders to vote on protocol changes. The execution of these decisions is carried out by the smart contract system, ensuring transparency and fairness
Also Read: How to Conduct a Smart Contract Audit
Challenges
-
Code Vulnerabilities:
Bugs in smart contract code can be exploited, leading to financial losses or security breaches.
-
Irreversibility:
Once deployed, mistakes or errors in smart contracts cannot be undone, making them final.
-
Scalability:
Smart contracts may struggle to handle large volumes of transactions efficiently.
-
Compliance:
Legal frameworks may not fully align with the autonomous nature of smart contracts, causing regulatory issues.
-
Oracle and Data Reliability:
Smart contracts rely on external data feeds (oracles), and inaccurate or manipulated data can lead to incorrect outcomes.
Also Read: Top Industry Leading Smart Contract Auditing Tools
Comparison with Traditional Systems
Let’s draw a comparison between smart contracts and traditional contracts, often written or verbal requiring multiple parties and extensive paperwork and documentation.
| Aspect | Smart Contracts | Traditional Contracts |
|---|---|---|
| Automation | Self-executing | Manual |
| Intermediaries | Few to none | Often required |
| Execution Time | Immediate | Manual, may take time |
| Cost Efficiency | Cost-effective | Costly |
| Transparency | High | Limited |
| Enforcement | Automatic (code-based) | Legal action required |
| Flexibility | Rigid once deployed | Can be renegotiated |
| Paperwork | Digital, no paperwork | Requires extensive documentation |
| Cash flow management | Automates cash flow; funds move upon condition fulfillment. | Managed manually; payments may be delayed. |
Future Prospects
The convergence of AI, IoT, and blockchain can enhance cash flow management by automating data collection and decision-making processes. This integration will allow for real-time adjustments to cash flow based on dynamic conditions, leading to improved efficiency.
The growth of DeFi platforms that leverage smart contracts will create more opportunities for automated cash flow management, allowing users to earn interest, lend, or borrow without intermediaries. This could lead to a more fluid and efficient financial ecosystem.
As governments and regulatory bodies start to recognize and create frameworks for smart contracts, their use in managing cash flow will become more standardized, facilitating broader acceptance and integration into traditional financial systems.
Conclusion
Smart contracts are essential for automating, securing, and optimizing cash flow management across industries, making fund management more efficient than ever. BlockApex, a leading smart contract audit company, offers services designed to streamline your transactions.
If you’re considering a smart contract audit and want to understand the smart contract audit cost, explore our process and book a free consultation today!