The blockchain world faces growing security threats, with honeypot scams being especially prevalent. In February 2024, a single cybercriminal stole $3.2 million across nine linked scams, using deceptive marketing and paid actors on Telegram. The incident highlights the scale of fraud, with hundreds or thousands of similar cases occurring.
In this blog, we’ll discuss honeypot scams and how they work. We’ll also dive into the attacker’s mindset, and learn the prevalent tactics to spot honeypots. Finally, we’ll see the steps on how to avoid falling victim, highlight common red flags, share some real-world examples, and explain what to do if you are scammed.
What are Honeypot Scams?
A honeypot scam in the crypto world is a fraudulent scheme where attackers create an attractive opportunity to lure victims into depositing their funds. Once the funds are in, victims discover they cannot withdraw or access their money.
An Analogy: Why are they called Honeypots?
The term “honeypot” comes from the idea of a pot of honey that draws in bees. Similarly, honeypot scams entice unsuspecting investors with promises of high returns or exclusive opportunities, only to ensnare them after they commit their funds.
“If it looks too sweet, it’s a honeypot treat — step back, don’t get caught in deceit!
The mantra above encapsulates this concept perfectly, highlighting how these scams may appear appealing but conceal hidden dangers. In the context of cryptocurrency. Honeypots are deceptive smart contracts designed to attract unwary investors with the promise of high returns, initially appearing legitimate.
However, they include hidden mechanisms that allow the scammer to mint tokens and drain the liquidity pool. Consequently, honeypot scams can either siphon off victims’ funds or block withdrawals. Due to technical vulnerabilities, psychological manipulation, and the complex nature of blockchain technology, even seasoned users can fall prey to such attacks.
How do Honeypot Scams work?
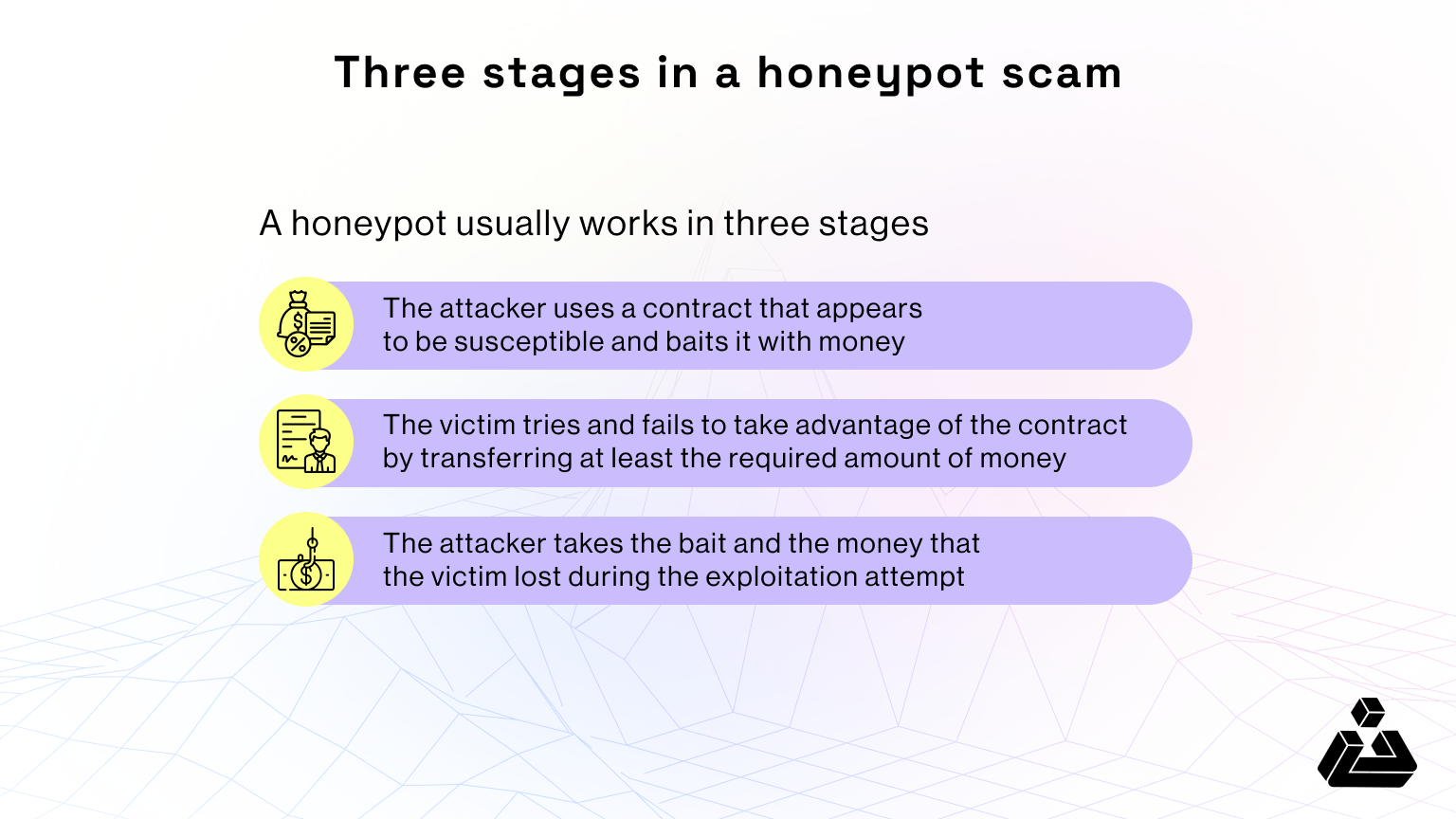
Honeypot scams operate through a carefully orchestrated lifecycle designed to lure even the most cautious investors. Understanding this lifecycle can help you protect your assets. The infographic below shows three main stages, on which we have elaborated below:
-
Contract Development: Crafting the Bait
It all begins with creating a seemingly legitimate smart contract. A savvy scammer embeds hidden traps, like withdrawal restrictions or hidden transfers, while ensuring small transactions work smoothly to maintain the illusion of trustworthiness.
-
Deployment: Luring Victims
Once ready, the scammer deploys the contract, seeding it with initial funds to appear legitimate. They aggressively market on different platforms via social media, forums, and even paid endorsements, creating hype and FOMO (fear of missing out)
-
Initial engagement: Building Trust
Early investors are allowed small withdrawals to build trust. As confidence grows, victims are encouraged to invest larger amounts, lured by seemingly favorable returns.
-
Exploitation: Springing the tap
When investors attempt significant withdrawals, the hidden mechanism activates, blocking withdrawals or transferring funds to the scammer’s wallet via bots.
-
Concealment: Covering tracks
To evade detection, scammers use complex code, multiple contracts, and fake transactions to obscure their tracks and keep the scam running longer.
-
Collapse: The Exit Strategy
Once the scammer drains enough funds, they shut down the contract and vanish, often moving on to launch new scams, learning from their past tricks.
Some prevalent tactics to spot honeypot
-
The Blacklist
One of the simplest honeypot scams is the blacklist tactic. Here’s how it works: once you buy the scam token, your wallet address is blacklisted. After that, any attempt to sell the token is blocked by the smart contract. Some scammers try to conceal the function under misleading names like “Approval for all”, but the goal remains the same-locking you into holding worthless tokens you can’t sell.
-
Balance manipulation
Another sneaky method is balance manipulation. Instead of outright halting you from selling, the smart contracts alter your token balance, showing you fewer tokens than you actually hold. So while you think you have your original balance intact, the contract makes it impossible to sell or transfer the full amount, leaving your investment stuck.
-
Minimum sell limit
In some scams, you are allowed to sell only if you meet a high threshold, which is often set to an impossible level. For instance, a scam might say you can sell only if you hold 10,000 tokens, but the total available supply is only 1000. Even if you try to buy more to meet the limit, you’ll be stuck in a never-ending loop, unable to sell tokens.
-
Scale of the problem
Honeypot scams are widespread, especially in an expanding Web3 market. Some scammers automate the process, creating hundreds or thousands of fraudulent contracts, For example, one scammer created 979 honeypot contracts in just two months. Though each victim may lose small amounts, like $60, the total adds up quickly. In this case, 979 contracts cost victims about $58,740 showing how small individual losses pile up to a big amount.
If you notice a project has very similar contracts or tokens being created rapidly (especially under suspicious names or copying well-known projects), it’s a warning sign.
Steps to Avoid Honeypot Scams
Pre-Investment checks
- Verify sources: Always confirm the legitimacy of websites, social media profiles, and project information. Scammers often use fake or misleading sites.
- Start small: If you are unsure about a project, make a small initial investment to test its legitimacy before committing larger amounts.
- Use Trusted Platforms: Stick to well-established and reputable exchanges and investment platforms to minimize risks.
Technical Precautions
-
- View Transaction History: Analyze smart contracts on platforms like Etherscan to identify any suspicious transactions or unusual code. A red flag can be unusual transaction patterns or a history of failed withdrawal attempts. A transaction history that suggests any transfers in are immediately transferred out (or, at least, shortly after) is a red flag.
- Audit: A trustworthy audit from a reputable company almost always eliminates the risk of a honeypot scam.
- Detection Tools: Tools like HoneyBadger, QuillCheck and Token Sniffer can help identify potential honeypot characteristics by scanning smart contracts for common red flags. While not infallible, they provide an additional layer of caution.
- Set Alerts: Use alert services to get notified of changes or updates in the smart contract or project status.
Common Red Flags
- Unrealistic Returns: If promised returns sound too good to be true, it probably is a red flag.
- Lack of Transparency: Projects that are vague about their team, location, or business model.
- Pressure Tactics: Scammers often create a sense of urgency to rush decisions using marketing tactics like Limited time offers, FOMO etc
- Poor Website and Communication: Look for professionalism in the project’s website and communications. Most scamming websites can be identified from inconsistent UI.
Real-world Example: Case Study
The Squid Game token honeypot scam took place in late October 2021 and became one of the most notorious crypto frauds of the year. Named after the popular Netflix show, the token (SQUID) attracted investors by capitalizing on the show’s immense popularity.
Key Details:
- Mechanism: The token was designed with a play-to-earn mechanism but was coded with malicious features that prevented holders from selling their tokens.
- Amount Lost: Investors collectively lost around $3.36 million as scammers exploited the hype and then executed a rug pull, draining liquidity.
- Scam Discovery: Investors began to realize they couldn’t sell their tokens due to hidden restrictions embedded in the contract, typical of a honeypot scam. They started speaking about this on Twitter and the $SQUID hashtag began trending.
- Aftermath: The token’s value skyrocketed to over $2,800 at its peak before plummeting to nearly zero within minutes as the scammers abandoned the project and disappeared.
What to Do If You Fall Victim
- Report the incident immediately: Reach out to relevant sources or where the scam occurred and report the incident.
- Seek Legal Advice: Consult with a lawyer who specializes in cryptocurrency and financial fraud.
- Alert the Community: Inform the crypto community through forums or channels like Discord where the crypto community is active and social media to prevent others from falling victim
Conclusion
Being vigilant and informed about the tactics used by scammers is essential to safeguard your assets and prevent falling victim to these deceptive schemes.
As these attacks become more prevalent, we at BlockApex believe that taking proactive steps, combined with continuous improvements in security protocols, will be critical in safeguarding the ecosystem from such malicious exploits.
Protect your project from any such attacks with smart contract auditing service. Mitigate weaknesses in your smart contract and improve its functionality with double line-to-line code analysis and a separate review by a lead auditor.