The ever-evolving digitization of online transactions has transformed our lives. We are now a touch away from performing even cross-border transactions. However, this shift of sheer convenience has also raised concerns about the security of customer data. Phishing scams and cyber attacks have exposed millions of stolen payment card numbers that find their way to the dark web for cheap prices. Hackers use these details to buy thousands of merchants on others’ card details causing a huge headache and loss for card issuers and customers. According to the FTC, in 2022, there were about 441,822 reported cases of credit card fraud, making it the most common type of theft.
Nevertheless, these hackers have found a million ways to scam people. However, what if these hackers never have our credit card numbers to begin with? That’s the magic of Tokenization. In our previous articles we have been constantly emphasizing on the importance of tokenization in the real world and credit cards are one of the most important applications of it.
In this article, we’re going to define credit card or payment tokenization and why it’s become a popular method for businesses to protect digital payment information.
What is Credit Card Tokenization?
The huge data breaches we hear mostly occur at the merchant’s end (which stores credit card data), not the banks or payment networks that handle the card transaction. With tokenization, we can remove this weakest link at the merchant’s end. The merchant now can only see the pseudorandom data that is worthless to them but enough to process the transaction at that time.
The essence of credit card tokenization is similar to a digital vault safeguarding all your precious information. Every time you go for online shopping, instead of showing your actual card number, a unique code, or token is shown to the merchants. This credit card token is what interacts with the payment ecosystem ensuring that even if it is attacked, it holds no intrinsic value to the bad actors in the system. This means that our actual card information is never shared in contactless payments, be it in-app or online. Cryptograms are another security layer implemented in payment systems to provide a unique value that helps verify the authenticity of each and every transaction.
What are the benefits of tokenization?
Tokenization offers several key benefits in enhancing data security and privacy. By replacing sensitive information, such as credit card numbers or personal details, with non-sensitive tokens, tokenization significantly reduces the risk of data breaches and fraud. This approach also helps organizations comply with regulatory requirements, like GDPR and PCI-DSS, by minimizing the storage and exposure of sensitive data.
Additionally, tokenization can improve customer trust and streamline payment processes. It also allows businesses to securely process transactions without directly handling sensitive information.
How Does Credit Card Tokenization Work?
We perform credit card tokenization by replacing the 15 or 16-digit card number with a unique randomly generated value called a “token.” This token is specific to the relationship between the payment processor and merchant and is securely stored in the payment gateway for further information. Here is what a typical run-down process of credit card tokenized transaction might look like:
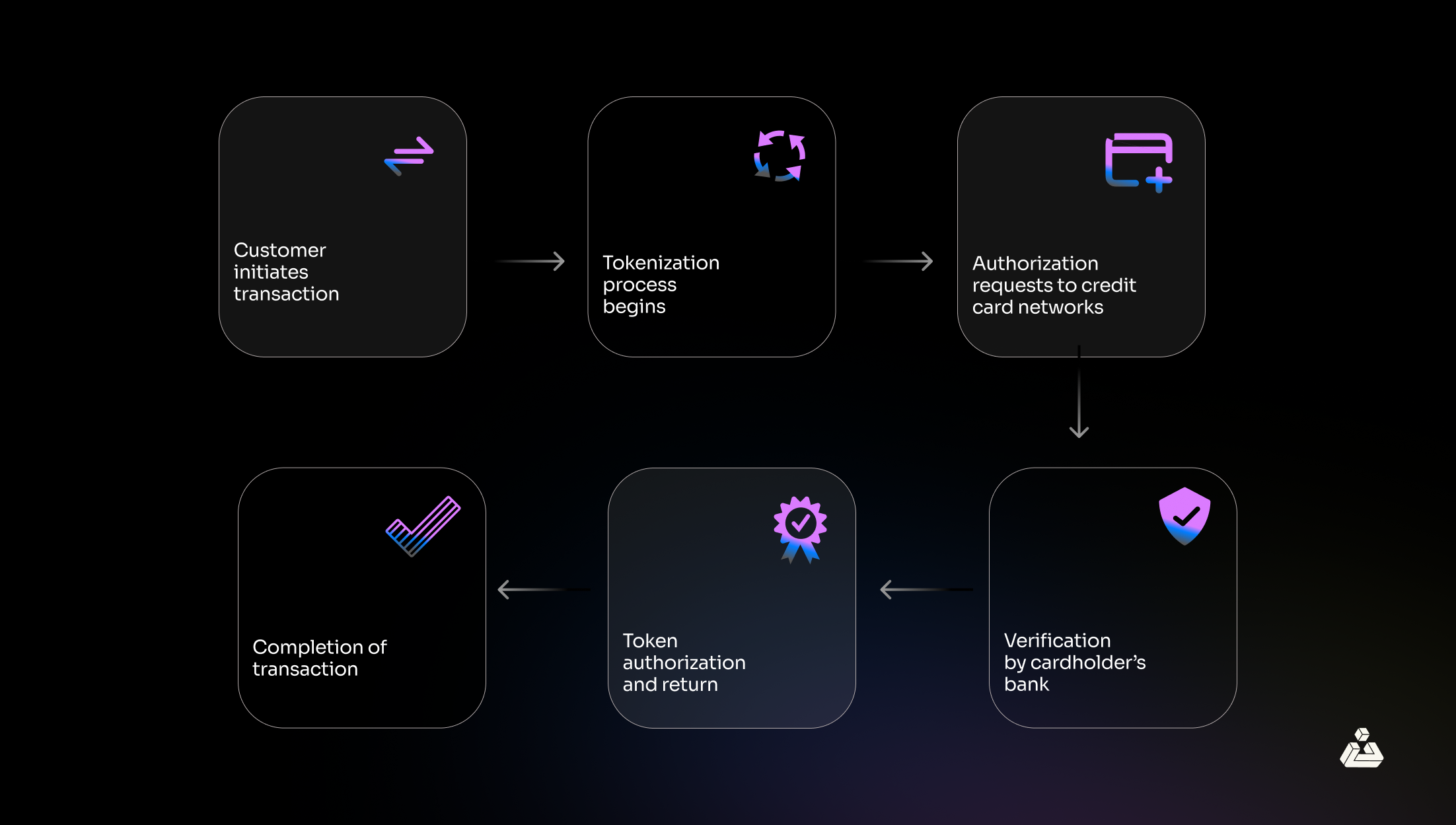
- The user first enters his details into a digital wallet such as Google wallets. The digital wallet then checks with the payment network to ensure that the card issuer is set up for tokenization and then requests to tokenize the card.
- The token service provider sends a message and required details to the card issuer who decides to approve the tokenization. The service provider can also ask for additional authentication like OTP.
- Once the token request is approved, the token service provider then securely sends the token, an image of your card, and a cryptographic key to the digital wallet, completing the activation process.
- So now if the customer initiates an online transaction, the user’s details are already in the digital wallet, and the transaction is initiated.
- The card data is tokenized by the service provider and sent back to the merchant bank.
- With the token in hand, the acquiring bank proceeds to request authorization from the credit card networks, such as Visa or Mastercard.
- Next, if the token supplied by the credit card issuer matches the account number, then the cardholder’s bank verifies the transaction.
- Upon approval, the issuer signals back with authorization and payment to the acquirer, confirming the token’s validity.
This entire process happens seamlessly in seconds and most of us don’t even notice the complexity behind it.
Where can Payment Tokens be Used?
Tokenization in ECommerce
Tokenization creates more opportunities for personalized payment experiences, where customers can save their preferences for future purchases. Since every merchant will be using different tokens for credit card information, there will be no chance of data breaches or sensitive information leakage. So even if your device is lost or stolen no data will be jeopardized as your device didn’t hold the real data.
One good example of this is Mastercard’s partnership with MetaMask. This is a significant advancement in the integration of cryptocurrencies into everyday payment methods. Through this collaboration, MetaMask users can now use their cryptocurrency holdings to make payments seamlessly, leveraging Mastercard’s vast payment network. This partnership allows users to directly convert their crypto into fiat currency at the time of transaction, enabling them to use their digital assets for a wide range of purchases, just like traditional money.
Online and In-app Purchases
We can also use our digital wallet to make in-app or website payments. These digital wallets use the same tap-and-go tech as contactless cards and can be used wherever contactless cards are accepted. Companies like Apple Pay and Google Pay utilize tokenization to protect user data, ensuring secure and seamless transactions for digital and mobile payments.
Online Guest Checkout
If a person does not frequently perform transactions and their card details are not stored on their wallets, then their card details can also be tokenized at guest checkout using a digital wallet like Click to Pay without needing to enter card details.
Business Benefits of Credit Card Tokenization
- Enhanced Security: By replacing sensitive credit card details with a non-sensitive token, businesses significantly reduce the risk of data breaches and fraud, protecting both their reputation and their customers’ trust.
- Regulatory Compliance: Tokenization helps businesses comply with data protection regulations, such as PCI DSS, by minimizing the storage and handling of sensitive card information, thereby reducing the scope and cost of compliance.
- Improved Customer Trust: By ensuring that customer payment data is protected, businesses can build and maintain trust, encouraging repeat purchases and customer loyalty.
- Reduced Liability and Fraud Risk: Since tokens cannot be used outside the specific environment they were created for, businesses reduce their liability in case of a data breach, as the tokenized data has no exploitable value.
- Streamlined Payment Processes: Tokenization allows for faster and more efficient payment processing, enhancing the overall customer experience and reducing cart abandonment rates for online and in-app purchases.
- Flexibility in Payment Methods: Tokenization supports a variety of payment methods, including recurring billing and one-click checkouts, providing a smoother and more convenient transaction experience for customers.
Credit Card Tokenization and Blockchain
Unlike traditional tokenization methods, which rely on centralized systems that can be vulnerable to breaches, blockchain provides a distributed ledger that records every transaction with cryptographic security. This decentralization means that even if one node is compromised, the overall system remains intact. Moreover, blockchain’s immutability ensures that once a token is created and recorded, it cannot be altered, reducing the risk of fraud and unauthorized access.
Additionally, smart contracts on blockchain can automate and enforce rules around token usage, further tightening security and streamlining processes.
Conclusion
As digital payments continue to grow and evolve, the use of tokenization is set to expand, offering even greater security and convenience for both businesses and consumers. In the future, we can expect tokenization to become a standard practice across various industries, further embedding itself as a critical component of digital payment infrastructure and helping to build a safer and more secure online economy.