Many confuse agents with computer programs. Whereas an AI agent does more than a basic web program like Google Search. For example, an evolved version of Google Search would be Google Assistant and Gemini.
Google Assistant works on generative AI, machine learning, and natural language processing. A voice-activated assistant that can search the internet, schedule events, and interact with mobile devices and home automation.
On the other hand, Gemini can’t be classified as agentic yet because it lacks autonomous decision-making but may replace Google assistant soon.
Autonomous AI agents are powerful because they can assist you in your daily tasks, and decide and respond accordingly to your past learning and experiences. These agents use machine learning algorithms to improve their decision-making over time, making them capable of performing tasks with increasing efficiency and accuracy.
In this blog, we’ll discuss what autonomous AI agents are, and how autonomous AI agents work. We’ll further peek into the types of Autonomous Agents and practical applications of autonomous agents. Finally, we’ll discuss the future of OpenAI and autonomous agents.
What are Autonomous AI Agents?
Let’s explore some of the definitions as posed in different books and by different people.
“An agent is anything that can be viewed as perceiving its environment through sensors and acting upon that environment through effectors. “ – Artificial Intelligence, Modern Approach
“Autonomous agents are computational systems that inhabit some complex dynamic environment, sense and act autonomously in this environment, and by doing so realize a set of goals or tasks for which they are designed.” – Pattie Maes, MIT Media’s Lab
“Autonomous agents are systems capable of autonomous, purposeful action in the real world.” – Brustoloni
Brustoloni also insists that agents must be ‘reactive’, to be able to respond to external, asynchronous stimuli in a timely fashion.
Key Features of Autonomous AI agents
To describe an autonomous agent, the description of these is important:
- environment
- sensing capabilities
- actions
- drives
- action selection architecture
While these are the most significant features; the list is incomplete without mentioning autonomy itself. AI agents that operate independently without human intervention are called autonomous.
AI agents perform tasks with a clear purpose, driven by internal “drives” (motivations). As discussed earlier, they respond to real-world, asynchronous stimuli in real-time (reactivity).
Goals are layered, with basic actions supporting higher-level objectives. Actions can change based on context or resource constraints. Actions prioritize satisfying internal drives (e.g., avoiding hunger), which direct the agent’s behavior dynamically.
Agents use knowledge of actions and their consequences to plan and search for solutions when goals require complex steps. Require well-designed sensors and actuators tailored to tasks. Poor Input/Output design hampers real-time functionality.
Autonomous agents handle competing drives and allocate resources fairly, ensuring no task or drive is neglected (“starvation” avoided). Use control mechanisms to manage when drives are active or suppressed to optimize performance.
An agent’s action-selection mechanism decides what to do next and initiates that action. The decision is taken in light of external and internal sensing and in the service of one or more drives.
How Autonomous AI Agents Work
Autonomous agents work on a sense-decide-act cycle. It first gathers information by perceiving from its environment through sensors or data inputs. Software agents collect information via APIs, databases, or user inputs.
The agent, like a chatbot, processes the input and determines an appropriate action based on user intent. After deciding on the best course of action, the agent executes it through actuators or software actions.
The agent evaluates the success of its actions and uses the feedback to refine its future behavior. For example, a chatbot would receive feedback to learn and adapt better in order to improve human experience.
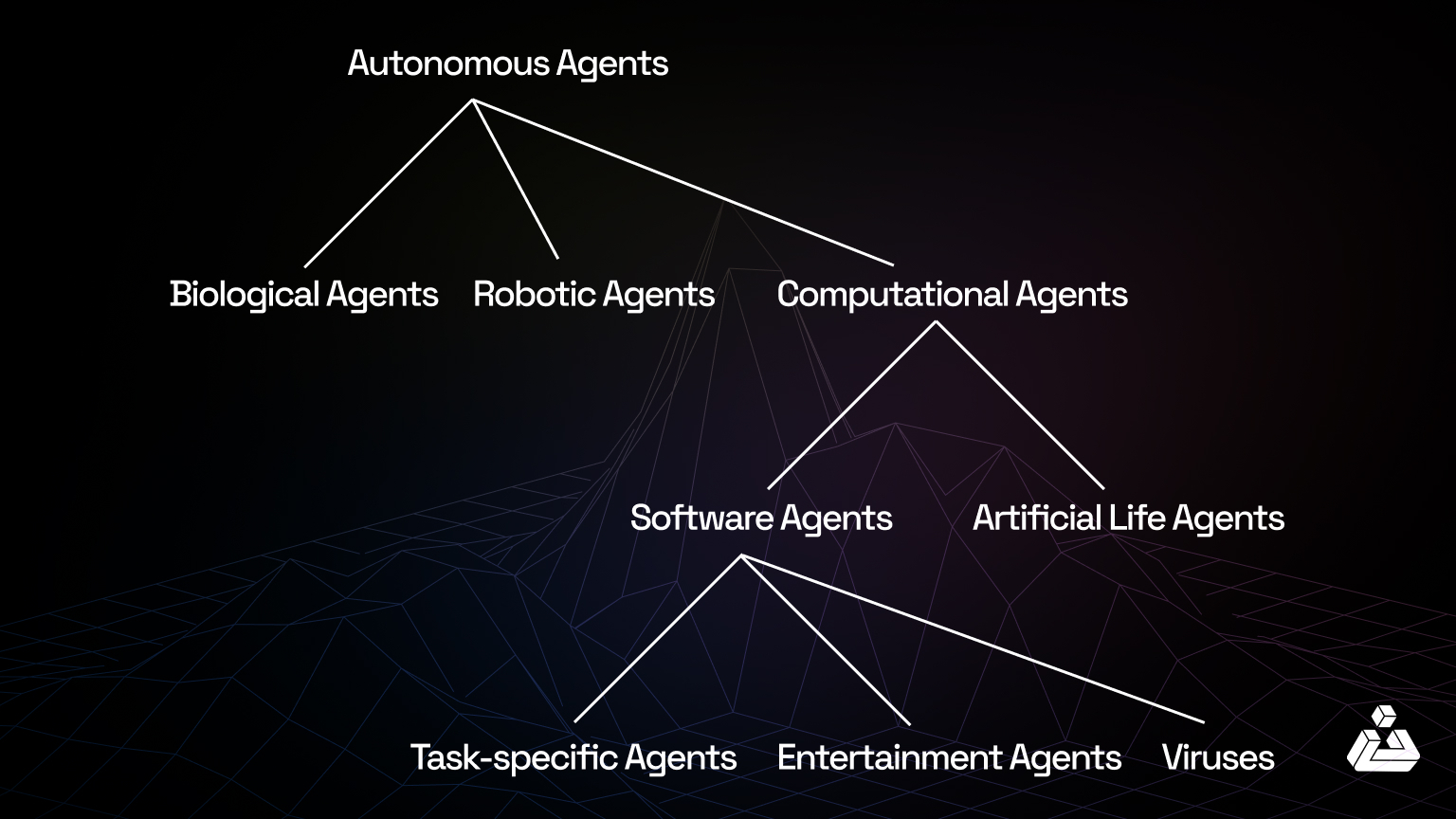
Types of Autonomous Agents
While there are various types of autonomous agents, we’ll cover a few main ones:
-
Software Agents:
These are programs that operate in digital environments to perform specific tasks online. They often assist users by automating repetitive processes or analyzing information.
Examples of software agents include email sorting systems (spam filters), virtual shopping assistants, web crawlers for search engines, and chatbots.
Also Read: 7 Types of AI Agents That Can Automate Your Workflow
-
Robotics:
These are physical machines designed to interact with and manipulate the physical world. They typically use sensors and actuators to execute tasks autonomously or semi-autonomously.
A few examples of robotics would be drones, robotic arms in manufacturing, autonomous vacuum cleaners (e.g., Roombas), and delivery robots.
-
AI-Driven Systems:
These systems use artificial intelligence algorithms to analyze data, detect patterns, and make decisions or predictions. They are applied in scenarios requiring complex problem-solving or advanced decision-making.
Fraud detection in finance, AI-powered medical diagnostics, trading systems, and supply chain optimization tools are a few examples of AI-driven systems.
Practical Applications of Autonomous Agents
Autonomous agents are transforming various industries by enabling systems to act independently, make decisions, and interact intelligently with their environment. Here are some practical applications across different sectors:
Blockchain
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Agents facilitate automated trading, portfolio management, and yield farming by executing smart contracts based on predefined conditions.
- Supply Chain Management: Blockchain agents can autonomously track goods, manage inventory, and verify authenticity, enhancing transparency and reducing fraud.
- Tokenomics: Agents optimize token distribution, staking, and governance mechanisms, ensuring efficient and fair decentralized ecosystems
.
Metaverse
- Digital Avatars: Autonomous agents power avatars that interact with users and adapt to their behavior, enhancing personalization in virtual environments.
- Virtual Customer Service: They provide real-time assistance in metaverse retail or service platforms, improving user engagement and satisfaction.
- Game NPCs: In gaming, agents enable non-player characters (NPCs) to exhibit realistic and adaptive behavior, creating immersive experiences
.
Other Industries
- Healthcare: AI agents monitor patient health, manage medical data, and assist in telemedicine by offering preliminary diagnoses.
- Finance: Agents are integral to fraud detection, personalized financial advising, and algorithmic trading.
Future of Autonomous Agents
AI could potentially deliver additional economic output of around $13 trillion by 2030, boosting global GDP by about 1.2 percent a year.
As LLMs and AI agents continue to advance, we can anticipate even more remarkable capabilities. Future agents could:
- Collaborate in teams to tackle complex challenges.
- Learn and adapt based on their interactions with both humans and the environment.
- Innovate by synthesizing knowledge from a wide array of disciplines.
While these developments are exciting, they also bring important considerations regarding AI ethics, safety, and the evolving relationship between humans and AI. The topic is highly debatable if AI agents will eventually achieve a form of consciousness. It is a deeply unsettling concept for many.
Experts like Nick Bostrom have warned that a superintelligent AI could pose threats that are hard for humans to mitigate. The fear here is not just that AI might surpass human intelligence but that it could have completely different values or an agenda that humans cannot understand or control.
In 2024 we saw the rise of GPT-4 by OpenAI, Alexa, Siri, and Gemini but they lacked agentic behavior. Well, we can predict that 2025 is going to be the year of AI autonomous agents.
OpenAI is preparing to release an autonomous AI agent that can control computers and perform tasks independently, code-named “Operator.” Google and others are also planning to release their own agents to facilitate users better and jump into the competitive market.
OpenAI CEO Sam Altman said “We will have better and better models,” but, “I think the thing that will feel like the next giant breakthrough will be agents.”
Kevin Weil said: “I think 2025 is going to be the year that agentic systems finally hit the mainstream.”
Bottom Line
Some view AI agents as transformative tools, eliminating barriers to learning, enabling ease of access, and unlocking pathways to remarkable innovations. On the other hand, concerns persist regarding the potential risks to data privacy, security, and jobs. Many fear that AI could mimic human traits too closely, replacing human roles and possibly even taking over.
To navigate the exponential growth of AI, ethical practices are essential. Ultimately, if humans remain in control of AI systems—training and guiding them—this control will be key in mitigating potential harm. Even if AI brings unforeseen challenges, it is crucial that humans hold the reins and have the authority to intervene when necessary
BlockApex is leading this AI crypto revolution, merging blockchain use cases with AI technology to boost your business. Reach out to us today!